Statistical feature extraction for artifact removal from concurrent fMRI-EEG recordings
- PMID: 22036675
- PMCID: PMC3254729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.042
Statistical feature extraction for artifact removal from concurrent fMRI-EEG recordings
Abstract
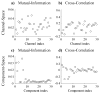
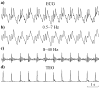
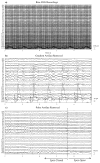
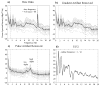
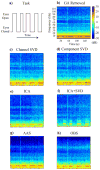
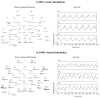
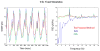
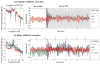
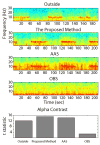
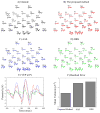
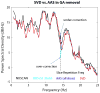
We propose a set of algorithms for sequentially removing artifacts related to MRI gradient switching and cardiac pulsations from electroencephalography (EEG) data recorded during functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Special emphasis is directed upon the use of statistical metrics and methods for the extraction and selection of features that characterize gradient and pulse artifacts. To remove gradient artifacts, we use channel-wise filtering based on singular value decomposition (SVD). To remove pulse artifacts, we first decompose data into temporally independent components and then select a compact cluster of components that possess sustained high mutual information with the electrocardiogram (ECG). After the removal of these components, the time courses of remaining components are filtered by SVD to remove the temporal patterns phase-locked to the cardiac timing markers derived from the ECG. The filtered component time courses are then inversely transformed into multi-channel EEG time series free of pulse artifacts. Evaluation based on a large set of simultaneous EEG-fMRI data obtained during a variety of behavioral tasks, sensory stimulations and resting conditions showed excellent data quality and robust performance attainable with the proposed methods. These algorithms have been implemented as a Matlab-based toolbox made freely available for public access and research use.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


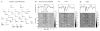
References
-
- Allen PJ, Josephs O, Turner R. A method for removing imaging artifact from continuous EEG recorded during functional MRI. Neuroimage. 2000;12:230–239. - PubMed
-
- Allen PJ, Polizzi G, Krakow K, Fish DR, Lemieux L. Identification of EEG events in the MR scanner: the problem of pulse artifact and a method for its subtraction. Neuroimage. 1998;8:229–239. - PubMed
-
- Anami K, Mori T, Tanaka F, Kawagoe Y, Okamoto J, Yarita M, Ohnishi T, Yumoto M, Matsuda H, Saitoh O. Stepping stone sampling for retrieving artifact-free electroencephalogram during functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage. 2003;19:281–295. - PubMed
-
- Bell AJ, Sejnowski TJ. An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Comput. 1995;7:1129–1159. - PubMed
-
- Benar CG, Aghakhani Y, Wang YH, Izenberg A, Al-Asmi A, Dubeau F, Gotman J. Quality of EEG in simultaneous EEG-fMRI for epilepsy. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2003;114:569–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

