5-hmC-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging
- PMID: 22037496
- PMCID: PMC3292193
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2959
5-hmC-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging
Abstract
DNA methylation dynamics influence brain function and are altered in neurological disorders. 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC), a DNA base that is derived from 5-methylcytosine, accounts for ∼40% of modified cytosine in the brain and has been implicated in DNA methylation-related plasticity. We mapped 5-hmC genome-wide in mouse hippocampus and cerebellum at three different ages, which allowed us to assess its stability and dynamic regulation during postnatal neurodevelopment through adulthood. We found developmentally programmed acquisition of 5-hmC in neuronal cells. Epigenomic localization of 5-hmC-regulated regions revealed stable and dynamically modified loci during neurodevelopment and aging. By profiling 5-hmC in human cerebellum, we found conserved genomic features of 5-hmC. Finally, we found that 5-hmC levels were inversely correlated with methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 dosage, a protein encoded by a gene in which mutations cause Rett syndrome. These data suggest that 5-hmC-mediated epigenetic modification is critical in neurodevelopment and diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
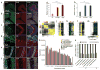



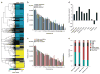
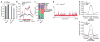
Comment in
-
Methylation on the mind.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Nov 23;14(12):1494-6. doi: 10.1038/nn.2988. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22119946 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jaenisch R, Bird A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals. Nat Genet. 2003;33(suppl):245–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P30 HD003352/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA129831/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MH076090/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- CA129831-03S1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071440/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS051630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051630/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM049245/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA129831/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH087977/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS067461/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32MH087977/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD064743/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R56 MH076090/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH076090/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG025688/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GM071440/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM049245/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

