Genetic variants associated with the white blood cell count in 13,923 subjects in the eMERGE Network
- PMID: 22037903
- PMCID: PMC3640990
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-011-1103-9
Genetic variants associated with the white blood cell count in 13,923 subjects in the eMERGE Network
Abstract
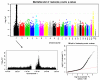
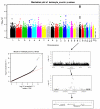
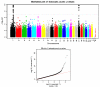
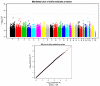
White blood cell count (WBC) is unique among identified inflammatory predictors of chronic disease in that it is routinely measured in asymptomatic patients in the course of routine patient care. We led a genome-wide association analysis to identify variants associated with WBC levels in 13,923 subjects in the electronic Medical Records and Genomics (eMERGE) Network. We identified two regions of interest that were each unique to subjects of genetically determined ancestry to the African continent (AA) or to the European continent (EA). WBC varies among different ancestry groups. Despite being ancestry specific, these regions were identifiable in the combined analysis. In AA subjects, the region surrounding the Duffy antigen/chemokine receptor gene (DARC) on 1q21 exhibited significant association (p value = 6.71e-55). These results validate the previously reported association between WBC and of the regulatory variant rs2814778 in the promoter region, which causes the Duffy negative phenotype (Fy-/-). A second missense variant (rs12075) is responsible for the two principal antigens, Fya and Fyb of the Duffy blood group system. The two variants, consisting of four alleles, act in concert to produce five antigens and subsequent phenotypes. We were able to identify the marginal and novel interaction effects of these two variants on WBC. In the EA subjects, we identified significantly associated SNPs tagging three separate genes in the 17q21 region: (1) GSDMA, (2) MED24, and (3) PSMD3. Variants in this region have been reported to be associated with WBC, neutrophil count, and inflammatory diseases including asthma and Crohn's disease.
Figures
References
-
- Altshuler D, Gibbs R, Peltonen L, Dermitzakis E, Schaffner S, Yu F, Bonnen P, de Bakker P, Deloukas P, Gabriel S, Gwilliam R, Hunt S, Inouye M, Jia X, Palotie A, Parkin M, Whittaker P, Chang K, Hawes A, Lewis L, Ren Y, Wheeler D, Muzny D, Barnes C, Darvishi K, Hurles M, Korn J, Kristiansson K, Lee C, McCarrol S, Nemesh J, Keinan A, Montgomery S, Pollack S, Price A, Soranzo N, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Anttila V, Brodeur W, Daly M, Leslie S, McVean G, Moutsianas L, Nguyen H, Zhang Q, Ghori M, McGinnis R, McLaren W, Takeuchi F, Grossman S, Shlyakhter I, Hostetter E, Sabeti P, Adebamowo C, Foster M, Gordon D, Licinio J, Manca M, Marshall P, Matsuda I, Ngare D, Wang V, Reddy D, Rotimi C, Royal C, Sharp R, Zeng C, Brooks L, McEwen J, Consortium IH. Integrating common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature. 2010;467:52–58. doi:10.1038/nature09298. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bach JF. The effect of infections on susceptibility to autoimmune and allergic diseases. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:911–920. doi:10.1056/NEJMra020100. - PubMed
-
- Barrett JC, Hansoul S, Nicolae DL, Cho JH, Duerr RH, Rioux JD, Brant SR, Silverberg MS, Taylor KD, Barmada MM, Bitton A, Dassopoulos T, Datta LW, Green T, Griffiths AM, Kistner EO, Murtha MT, Regueiro MD, Rotter JI, Schumm LP, Steinhart AH, Targan SR, Xavier RJ, Libioulle C, Sandor C, Lathrop M, Belaiche J, Dewit O, Gut I, Heath S, Laukens D, Mni M, Rutgeerts P, Van Gossum A, Zelenika D, Franchimont D, Hugot JP, de Vos M, Vermeire S, Louis E, Cardon LR, Anderson CA, Drummond H, Nimmo E, Ahmad T, Prescott NJ, Onnie CM, Fisher SA, Marchini J, Ghori J, Bumpstead S, Gwilliam R, Tremelling M, Deloukas P, Mansfield J, Jewell D, Satsangi J, Mathew CG, Parkes M, Georges M, Daly MJ. Genomewide association defines more than 30 distinct susceptibility loci for Crohn’s disease. Nat Genet. 2008;40:955–962. doi:10.1038/ng.175. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barrett JC, Clayton DG, Concannon P, Akolkar B, Cooper JD, Erlich HA, Julier C, Morahan G, Nerup J, Nierras C, Plagnol V, Pociot F, Schuilenburg H, Smyth DJ, Stevens H, Todd JA, Walker NM, Rich SS. Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2009;41:703–707. doi:10.1038/ng.381. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HG004603/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004603/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004424/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004609/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG04599/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004610/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG004424/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG006375/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004438/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG004608/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004599/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG004609/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG06781/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HG004610/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004608/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

