Influence of radiology report format on reading time and comprehension
- PMID: 22038513
- PMCID: PMC3264711
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-011-9424-8
Influence of radiology report format on reading time and comprehension
Abstract
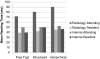
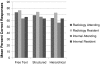
This study examined whether radiology report format influences reading time and comprehension of information. Three reports were reformatted to conventional free text, structured text organized by organ system, and hierarchical structured text organized by clinical significance. Five attending radiologists, five radiology residents, five internal medicine attendings, and five internal medicine residents read the reports and answered a series of questions about them. Reading was timed and participants reported reading preferences. For reading time, there was no significant effect for format, but there was for attending versus resident, and radiology versus internal medicine. For percent correct scores, there was no significant effect for report format or for attending versus resident, but there was for radiology versus internal medicine with the radiologists scoring better overall. Report format does not appear to impact viewing time or percent correct answers, but there are differences in both for specialty and level of experience. There were also differences between the four groups of participants with respect to what they focus on in a radiology report and how they read reports (skim versus read in detail). There may not be a "one-size-fits-all" radiology report format as individual preferences differ widely.
Figures
Similar articles
-
24/7/365 Neuroradiologist Coverage Improves Resident Perception of Educational Experience, Referring Physician Satisfaction, and Turnaround Time.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2020 May-Jun;49(3):168-172. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2020. PMID: 30391225
-
Improving communication of diagnostic radiology findings through structured reporting.Radiology. 2011 Jul;260(1):174-81. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11101913. Epub 2011 Apr 25. Radiology. 2011. PMID: 21518775 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement in reporting skills of radiology residents with a structured reporting curriculum.Acad Radiol. 2014 Jan;21(1):126-33. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2013.10.007. Acad Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24331275
-
Overnight Resident versus 24-hour Attending Radiologist Coverage in Academic Medical Centers.Radiology. 2018 Dec;289(3):809-813. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018180690. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Radiology. 2018. PMID: 30277849 Review.
-
Overnight resident interpretation of torso CT at a level 1 trauma center an analysis and review of the literature.Acad Radiol. 2009 Sep;16(9):1155-60. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2009.02.017. Epub 2009 May 30. Acad Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19481962 Review.
Cited by
-
Redefining the structure of structured reporting in radiology.Insights Imaging. 2020 Feb 4;11(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13244-019-0831-6. Insights Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32020396 Free PMC article.
-
Eye-tracking differences between free text and template radiology reports: a pilot study.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2023 Feb;10(Suppl 1):S11902. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.10.S1.S11902. Epub 2023 Feb 8. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2023. PMID: 36761037 Free PMC article.
-
Time Is Money: Considerations for Measuring the Radiological Reading Time.J Imaging. 2022 Jul 24;8(8):208. doi: 10.3390/jimaging8080208. J Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35893086 Free PMC article.
-
Structured reports of pelvic magnetic resonance imaging in primary endometrial cancer: Potential benefits for clinical decision-making.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 25;14(3):e0213928. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213928. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30908525 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicians' Behavior Toward Radiology Reports: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2020 Nov 5;12(11):e11336. doi: 10.7759/cureus.11336. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33304672 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kroken P. (2008). The radiology report: a new look at an old standard. Radiol Manag March/April:39–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical