Discovery of an ebolavirus-like filovirus in europe
- PMID: 22039362
- PMCID: PMC3197594
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002304
Discovery of an ebolavirus-like filovirus in europe
Abstract
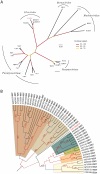
Filoviruses, amongst the most lethal of primate pathogens, have only been reported as natural infections in sub-Saharan Africa and the Philippines. Infections of bats with the ebolaviruses and marburgviruses do not appear to be associated with disease. Here we report identification in dead insectivorous bats of a genetically distinct filovirus, provisionally named Lloviu virus, after the site of detection, Cueva del Lloviu, in Spain.
Conflict of interest statement
Stephen Hutchison is an employee at 454 Life Sciences, a division of Roche Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Barrette RW, Metwally SA, Rowland JM, Xu L, Zaki SR, et al. Discovery of swine as a host for the Reston ebolavirus. Science. 2009;325:204–206. - PubMed
-
- Leroy EM, Epelboin A, Mondonge V, Pourrut X, Gonzalez JP, et al. Human Ebola outbreak resulting from direct exposure to fruit bats in Luebo, Democratic Republic of Congo, 2007. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2009;9:723–728. - PubMed
-
- Leroy EM, Kumulungui B, Pourrut X, Rouquet P, Hassanin A, et al. Fruit bats as reservoirs of Ebola virus. Nature. 2005;438:575–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

