A robust and rapid method of producing soluble, stable, and functional G-protein coupled receptors
- PMID: 22039398
- PMCID: PMC3201940
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023036
A robust and rapid method of producing soluble, stable, and functional G-protein coupled receptors
Abstract
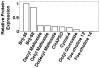
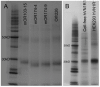
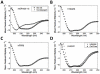
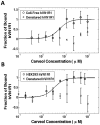
Membrane proteins, particularly G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs), are notoriously difficult to express. Using commercial E. coli cell-free systems with the detergent Brij-35, we could rapidly produce milligram quantities of 13 unique GPCRs. Immunoaffinity purification yielded receptors at >90% purity. Secondary structure analysis using circular dichroism indicated that the purified receptors were properly folded. Microscale thermophoresis, a novel label-free and surface-free detection technique that uses thermal gradients, showed that these receptors bound their ligands. The secondary structure and ligand-binding results from cell-free produced proteins were comparable to those expressed and purified from HEK293 cells. Our study demonstrates that cell-free protein production using commercially available kits and optimal detergents is a robust technology that can be used to produce sufficient GPCRs for biochemical, structural, and functional analyses. This robust and simple method may further stimulate others to study the structure and function of membrane proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Klammt C, Löhr F, Schäfer B, Haase W, Dötsch V, et al. High level cell-free expression and specific labeling of integral membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:568–580. - PubMed
-
- Klammt C, Schwarz D, Fendler K, Haase W, Dotsch V, et al. Evaluation of detergents for the soluble expression of alpha-helical and beta-barrel-type integral membrane proteins by a preparative scale individual cell-free expression system. FEBS J. 2005;272:6024–6038. - PubMed
-
- Klammt C, Schwarz D, Eifler N, Engel A, Piehler J, et al. Cell-free production of G protein-coupled receptors for functional and structural studies. J Struct Biol. 2007;158:482–493. - PubMed
-
- Klammt C, Srivastava A, Eifler N, Junge F, Beyermann M, et al. Functional analysis of cell-free-produced human endothelin B receptor reveals transmembrane segment 1 as an essential area for ET-1 binding and homodimer formation. FEBS J. 2007;274:3257–3269. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz D, Junge F, Durst F, Frölich N, Schneider B, et al. Preparative scale expression of membrane proteins in Escherichia coli-based continuous exchange cell-free systems. Nat Protoc. 2007;2:2945–2957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

