Imprinted genes that regulate early mammalian growth are coexpressed in somatic stem cells
- PMID: 22039481
- PMCID: PMC3198398
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026410
Imprinted genes that regulate early mammalian growth are coexpressed in somatic stem cells
Abstract
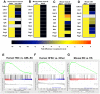
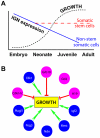
Lifelong, many somatic tissues are replenished by specialized adult stem cells. These stem cells are generally rare, infrequently dividing, occupy a unique niche, and can rapidly respond to injury to maintain a steady tissue size. Despite these commonalities, few shared regulatory mechanisms have been identified. Here, we scrutinized data comparing genes expressed in murine long-term hematopoietic stem cells with their differentiated counterparts and observed that a disproportionate number were members of the developmentally-important, monoallelically expressed imprinted genes. Studying a subset, which are members of a purported imprinted gene network (IGN), we found their expression in HSCs rapidly altered upon hematopoietic perturbations. These imprinted genes were also predominantly expressed in stem/progenitor cells of the adult epidermis and skeletal muscle in mice, relative to their differentiated counterparts. The parallel down-regulation of these genes postnatally in response to proliferation and differentiation suggests that the IGN could play a mechanistic role in both cell growth and tissue homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Wilson A, Laurenti E, Oser G, van der Wath RC, Blanco-Bose W, et al. Hematopoietic stem cells reversibly switch from dormancy to self-renewal during homeostasis and repair. Cell. 2008;135:1118–1129. - PubMed
-
- Dhawan J, Rando TA. Stem cells in postnatal myogenesis: molecular mechanisms of satellite cell quiescence, activation and replenishment. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:666–673. - PubMed
-
- Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, et al. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature. 2007;449:1003–1007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- F32 HL086223/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR059122/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB005173/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- EB005173/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058192/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036562/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK060445/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK060445/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL086223/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK58192/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AG034451/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG034451/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1RC2AG036562/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA126752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50CA126752/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

