Tau enhances α-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in cellular models of synucleinopathy
- PMID: 22039514
- PMCID: PMC3200341
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026609
Tau enhances α-synuclein aggregation and toxicity in cellular models of synucleinopathy
Abstract
Background: The simultaneous accumulation of different misfolded proteins in the central nervous system is a common feature in many neurodegenerative diseases. In most cases, co-occurrence of abnormal deposited proteins is observed in different brain regions and cell populations, but, in some instances, the proteins can be found in the same cellular aggregates. Co-occurrence of tau and α-synuclein (α-syn) aggregates has been described in neurodegenerative disorders with primary deposition of α-syn, such as Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Although it is known that tau and α-syn have pathological synergistic effects on their mutual fibrillization, the underlying biological effects remain unclear.
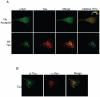
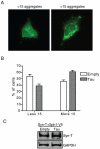
Methodology/principal findings: We used different cell models of synucleinopathy to investigate the effects of tau on α-syn aggregation. Using confocal microscopy and FRET-based techniques we observed that tau colocalized and interacted with α-syn aggregates. We also found that tau overexpression changed the pattern of α-syn aggregation, reducing the size and increasing the number of aggregates. This shift was accompanied by an increase in the levels of insoluble α-syn. Furthermore, co-transfection of tau increased secreted α-syn and cytotoxicity.
Conclusions/significance: Our data suggest that tau enhances α-syn aggregation and toxicity and disrupts α-syn inclusion formation. This pathological synergistic effect between tau and α-syn may amplify the deleterious process and spread the damage in neurodegenerative diseases that show co-occurrence of both pathologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

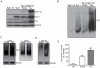

References
-
- Chartier-Harlin MC, Kachergus J, Roumier C, Mouroux V, Douay X, et al. Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2004;364:1167–1169. - PubMed
-
- Ibanez P, Bonnet AM, Debarges B, Lohmann E, Tison F, et al. Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 2004;364:1169–1171. - PubMed
-
- Kruger R, Kuhn W, Muller T, Woitalla D, Graeber M, et al. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat Genet. 1998;18:106–108. - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997;276:2045–2047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

