Antioxidant properties of lutein contribute to the protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced uveitis in mice
- PMID: 22040935
- PMCID: PMC3217882
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8546-6-38
Antioxidant properties of lutein contribute to the protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced uveitis in mice
Abstract
Background: Lutein is an important eye-protective nutrient. This study investigates the protective effects and mechanisms of lutein on lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced uveitis in mice.
Methods: Lutein, suspended in drinking water at a final concentration of 12.5 and 25 mg/mL, was administered to mice at 0.1 mL/10 g body weight for five consecutive days. Control and model group received drinking water only. Uveitis was induced by injecting LPS (100 mg per mouse) into the footpad in the model and lutein groups on day 5 after the last drug administration. Eyes of the mice were collected 24 hours after the LPS injection for the detection of indicators using commercial kits and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
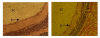
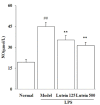
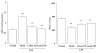
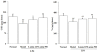
Results: LPS-induced uveitis was confirmed by significant pathological damage and increased the nitric oxide level in eye tissue of BALB/C mice 24 hours after the footpad injection. The elevated nitric oxide level was significantly reduced by oral administration of lutein (125 and 500 mg/kg/d for five days) before LPS injection. Moreover, lutein decreased the malondialdehyde content, increased the oxygen radical absorbance capacity level, glutathione, the vitamin C contents and total superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities. Lutein further increased expressions of copper-zinc SOD, manganese SOD and GPx mRNA. Conclusion The antioxidant properties of lutein contribute to the protection against LPS-induced uveitis, partially through the intervention of inflammation process.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective effects of bilberry ( Vaccinium myrtillus L.) extract against endotoxin-induced uveitis in mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Apr 28;58(8):4731-6. doi: 10.1021/jf904572a. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20222750
-
[Study on inhibitory effect of lycium pigment on lipopolysaccharide-induced uveitis in rats and its mechanism].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013 Jun;38(11):1778-82. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24010295 Chinese.
-
Inhibitory effects of lutein on endotoxin-induced uveitis in Lewis rats.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Jun;47(6):2562-8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-1429. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16723471
-
Assessment of Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Dimethylglycine Sodium Salt and Its Role in Providing Protection against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mice.PLoS One. 2016 May 12;11(5):e0155393. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155393. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27171376 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of an antioxidant, lutein, during retinal inflammation.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Mar;50(3):1433-9. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-2493. Epub 2008 Nov 7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 18997089
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Potential Therapeutic Use of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides in Disease.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Feb 12;2019:4615745. doi: 10.1155/2019/4615745. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30891458 Free PMC article.
-
Gloeothece sp.-Exploiting a New Source of Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antitumor Agents.Mar Drugs. 2021 Nov 4;19(11):623. doi: 10.3390/md19110623. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34822494 Free PMC article.
-
Lutein Encapsulated in PLGA-Phospholipid Nano-Carrier Effectively Mitigates Cytokines by Inhibiting Tumor Necrosis Factor TNF-α and Nuclear Factor NF-κB in Mice Retina.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Apr 3;14(4):197. doi: 10.3390/jfb14040197. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37103287 Free PMC article.
-
Lutein dietary supplementation attenuates streptozotocin-induced testicular damage and oxidative stress in diabetic rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Jun 30;15:204. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0693-5. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26122042 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of aqueous extract of germinated and fermented mung bean on ethanol-mediated liver damage.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:693613. doi: 10.1155/2013/693613. Epub 2012 Dec 24. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23484140 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

