Thrombolysis for massive pulmonary embolism in pregnancy: a case report
- PMID: 22041192
- PMCID: PMC3222602
- DOI: 10.1186/1865-1380-4-69
Thrombolysis for massive pulmonary embolism in pregnancy: a case report
Abstract
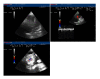
Mortality from pulmonary embolism (PE) in pregnancy might be related to challenges in targeting the right population for prevention. Such targeting could help ensure that the correct diagnosis is suspected and adequately investigated, and allow the initiation of the timely and best possible treatment of this disease. In the literature to date only 18 case reports of thrombolysis in pregnant women with PE have been reported, and showed beneficial effects for both mother and fetus in terms of mortality and complications with acceptable bleeding risks. We present here the case of a pregnant patient with massive PE who underwent successful thrombolysis. A 26-year-old pregnant (at 24 weeks) woman was admitted 4 h after onset of sudden acute dyspnea and chest pain. An immediate electrocardiogram showed a typical S1-Q3-T3 pattern. The echocardiogram showed a distended right ventricle with free-wall hypokinesia and displacement of the interventricular septum toward the left ventricle. Thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (alteplase 10 mg bolus, then 90 mg over 2 h) was administered. Pelvic examination and ultrasound showed regular fetal heart beat, and regular placental and liquid presence. No problems developed for the mother or fetus in the subsequent days or at discharge. In conclusion, in pregnant patients with life-threatening massive PE, thrombolytic therapy can be administered, and the use of echocardiographic, laboratory, and clinical data can be useful tools to achieve a rapid diagnosis and make a therapeutic decision, but additional studies need to be performed to further define its use.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of bivalirudin for heparin-induced thrombocytopaenia after thrombolysis in massive pulmonary embolism: a case report.Int J Emerg Med. 2010 Jul 21;3(3):197-9. doi: 10.1007/s12245-010-0193-9. Int J Emerg Med. 2010. PMID: 21031046 Free PMC article.
-
Successful low-dosage thrombolysis of massive pulmonary embolism in primigravida: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Oct;97(43):e12985. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012985. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30412129 Free PMC article.
-
An unusual presentation of massive pulmonary embolism mimicking septal acute myocardial infarction treated with tenecteplase.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2009 Feb;27(2):215-9. doi: 10.1007/s11239-007-0185-7. Epub 2008 Jan 9. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2009. PMID: 18183355
-
Should thrombolytic therapy be used in patients with pulmonary embolism?Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2004;4(2):69-74. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200404020-00001. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15049719 Review.
-
Successful thrombolytic therapy of post-operative massive pulmonary embolism after ultralong cardiopulmonary resuscitation: a case report and review of literature.Clin Respir J. 2017 May;11(3):383-390. doi: 10.1111/crj.12332. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Clin Respir J. 2017. PMID: 26083151 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of Cardiac Arrest in the Pregnant Patient.Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Jun 19;20(7):57. doi: 10.1007/s11936-018-0652-9. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29922883 Review.
-
Pulmonary embolism in pregnancy.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014 Apr;37(3):251-70. doi: 10.1007/s11239-013-0941-9. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014. PMID: 23689957 Review.
-
Successful thrombolysis of stroke with intravenous alteplase in the third trimester of pregnancy.J Neurol. 2014 Mar;261(3):632-4. doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7286-y. Epub 2014 Feb 26. J Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24570282 No abstract available.
-
The use of thrombolytic therapy in pregnancy.Obstet Med. 2013 Sep;6(3):105-111. doi: 10.1177/1753495X13488771. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Obstet Med. 2013. PMID: 27708701 Free PMC article.
-
Successfully conservative management of the uterus in acute pulmonary embolism during cesarean section for placenta previa: a case report from Tu Du Hospital, Vietnam and literature review.Int J Emerg Med. 2024 Jan 29;17(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12245-024-00587-4. Int J Emerg Med. 2024. PMID: 38287235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fasullo S, Scalzo S, Maringhini G, Ganci F, Cannizzaro S, Basile I, Cangemi D, Terrazzino G, Parrinello G, Sarullo FM, Baglin R, Paterna S, Di Pasquale P. Six-Month Echocardiographic Study in Patients With Submassive Pulmonary Embolism and Right Ventricle Dysfunction: Comparison of Thrombolysis With Heparin. Am J Med Sci. 2011;341(1):33–9. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3181f1fc3e. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stein PD, Hull RD, Raskob G. Risks for major bleeding from thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: consideration of noninvasive management. Ann Intern Med. 1994;121:313–7. - PubMed
-
- Torbicki A, Perrier A, Konstantinides S, Torbicki A, Perrier A, Konstantinides S, Agnelli G, Galiè N, Pruszczyk P, Bengel F, Brady AJ, Ferreira D, Janssens U, Klepetko W, Mayer E, Remy-Jardin M, Bassand JP. ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG) Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2008;29:2276–315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources