Upregulation of micro RNA-146a (miRNA-146a), a marker for inflammatory neurodegeneration, in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD) and Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker (GSS) syndrome
- PMID: 22043907
- PMCID: PMC3719866
- DOI: 10.1080/15287394.2011.618973
Upregulation of micro RNA-146a (miRNA-146a), a marker for inflammatory neurodegeneration, in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD) and Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker (GSS) syndrome
Abstract
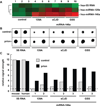
A mouse- and human-brain-abundant, nuclear factor (NF)-кB-regulated, micro RNA-146a (miRNA-146a) is an important modulator of the innate immune response and inflammatory signaling in specific immunological and brain cell types. Levels of miRNA-146a are induced in human brain cells challenged with at least five different species of single- or double-stranded DNA or RNA neurotrophic viruses, suggesting a broad role for miRNA-146a in the brain's innate immune response and antiviral immunity. Upregulated miRNA-146a is also observed in pro-inflammatory cytokine-, Aβ42 peptide- and neurotoxic metal-induced, oxidatively stressed human neuronal-glial primary cell cocultures, in murine scrapie and in Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain. In AD, miRNA-146a levels are found to progressively increase with disease severity and co-localize to brain regions enriched in inflammatory neuropathology. This study provides evidence of upregulation of miRNA-146a in extremely rare (incidence 1-10 per 100 million) human prion-based neurodegenerative disorders, including sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD) and Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome (GSS). The findings suggest that an upregulated miRNA-146a may be integral to innate immune or inflammatory brain cell responses in prion-mediated infections and to progressive and irreversible neurodegeneration of both the murine and human brain.
Figures

References
-
- Alexandrov PN, Zhao Y, Pogue AI, Tarr MA, Kruck TP, Percy ME, Cui JG, Lukiw WJ. Synergistic effects of iron and aluminum on stress-related gene expression in primary human neural cells. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2005;8:117–127. - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Fluiter K, Iyer A, Zurolo E, Vreijling J, van Vliet EA, Baayen JC, Gorter JA. Expression pattern of miR-146a, an inflammation-associated microRNA, in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010;31:1100–1107. - PubMed
-
- Burmistrova OA, Goltsov AY, Abramova LI, Kaleda VG, Orlova VA, Rogaev EI. MicroRNA in schizophrenia: Genetic and expression analysis of miR-130b (22q11) Biochemistry (Moscow) 2007;72:578–582. - PubMed
-
- Collins S, McLean CA, Masters CL. Gerstmann–Sträussler–Scheinker syndrome, fatal familial insomnia, and kuru: A review of these less common human transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2001;8:387–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
