CD4+ T helper 2 cells--microbial triggers, differentiation requirements and effector functions
- PMID: 22043920
- PMCID: PMC3230791
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03497.x
CD4+ T helper 2 cells--microbial triggers, differentiation requirements and effector functions
Abstract
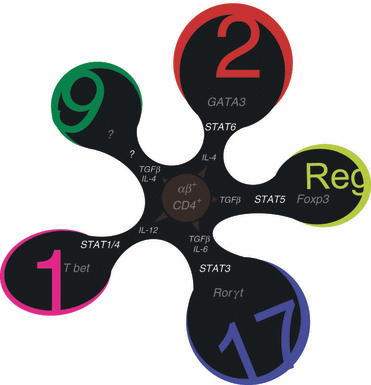
Over the past 10 years we have made great strides in our understanding of T helper cell differentiation, expansion and effector functions. Within the context of T helper type 2 (Th2) cell development, novel innate-like cells with the capacity to secrete large amounts of interleukin-5 (IL-5), IL-13 and IL-9 as well as IL-4-producing and antigen-processing basophils have (re)-emerged onto the type 2 scene. To what extent these new players influence αβ+ CD4+ Th2 cell differentiation is discussed throughout this appraisal of the current literature. We highlight the unique features of Th2 cell development, highlighting the three necessary signals, T-cell receptor ligation, co-stimulation and cytokine receptor ligation. Finally, putting these into context, microbial and allergenic properties that trigger Th2 cell differentiation and how these influence Th2 effector function are discussed and questioned.
© 2011 The Authors. Immunology © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
T helper 2 (Th2) cell differentiation, type 2 innate lymphoid cell (ILC2) development and regulation of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13 production.Cytokine. 2015 Sep;75(1):14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.05.010. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 26044597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Metabolic Requirements of Th2 Cell Differentiation.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 27;10:2318. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02318. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31611881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Germinal centers regulate human Th2 development.J Immunol. 2003 Aug 15;171(4):1657-66. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.4.1657. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12902463
-
Understanding the roles of basophils: breaking dawn.Immunology. 2012 Mar;135(3):192-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03530.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22044049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4 cell-secreted, posttranslationally modified cytokine GIF suppresses Th2 responses by inhibiting the initiation of IL-4 production.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 9;105(49):19402-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810035105. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19036925 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tailored immune responses: novel effector helper T cell subsets in protective immunity.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Feb 20;10(2):e1003905. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003905. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24586147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pretreatment with glycomacropeptide reduces allergen sensitization, alleviates immediate cutaneous hypersensitivity and protects from anaphylaxis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2012 Oct;170(1):18-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04631.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22943197 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamics of the inflammatory response during BBN-induced bladder carcinogenesis in mice.J Transl Med. 2019 Nov 28;17(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-02146-5. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31779626 Free PMC article.
-
The Hodgkin Lymphoma Immune Microenvironment: Turning Bad News into Good.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 7;14(5):1360. doi: 10.3390/cancers14051360. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Immune Cells in Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and Remodeling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 23;9:659666. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.659666. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34368120 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136:2348–57. - PubMed
-
- Veldhoen M, Uyttenhove C, van Snick J, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta ‘reprograms’ the differentiation of T helper 2 cells and promotes an interleukin 9-producing subset. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:1341–6. - PubMed
-
- Hegazy AN, Peine M, Helmstetter C, et al. Interferons direct Th2 cell reprogramming to generate a stable GATA-3+ T-bet+ cell subset with combined Th2 and Th1 cell functions. Immunity. 2010;32:116–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

