Role of the inflammatory protein serine protease inhibitor Kazal in preventing cytolytic granule granzyme A-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 22043941
- PMCID: PMC3230794
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03498.x
Role of the inflammatory protein serine protease inhibitor Kazal in preventing cytolytic granule granzyme A-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
Serine protease inhibitor Kazal (SPIK) is an inflammatory protein whose levels are elevated in numerous cancers. However, the role of this protein in cancer development is unknown. We have recently found that SPIK suppresses serine protease-dependent cell apoptosis. Here, we report that anti-SPIK antibodies can co-immmunoprecipitate serine protease granzyme A (GzmA), a cytolytic granule secreted by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells during immune surveillance, and that SPIK suppresses GzmA-induced cell apoptosis. Deletion studies show that the C3-C4 region of SPIK is critical for this suppression. These studies suggest that over-expression of SPIK may prevent GzmA-mediated immune-killing, thereby establishing the tolerance of cancer cells to the body's immune surveillance system. Suppression of over-expressed SPIK can restore the susceptibility of these cells to apoptotic death triggered by GzmA. This finding implies that it is possible to overcome tolerance of cancer cells to the body's immune surveillance system and restore the GzmA-mediated immune-killing by suppressing the over-expression of SPIK.
© 2011 The Authors. Immunology © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
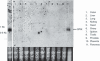


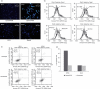
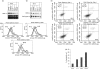

References
-
- Stenman UH. Tumor-associated trypsin inhibitor. Clin Chem. 2002;48:1206–9. - PubMed
-
- Greene LJ. Pancreatic exocrine secretory proteins. J Surg Oncol. 1975;7:151–4. - PubMed
-
- Tomita N, Doi S, Higashiyama M, et al. Expression of pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor gene in human colorectal tumor. Cancer. 1990;66:2144–9. - PubMed
-
- Ohmachi Y, Murata A, Matsuura N, et al. Specific expression of the pancreatic-secretory-trypsin-inhibitor (PSTI) gene in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1993;55:728–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

