Insights into the initiation of type 2 immune responses
- PMID: 22044021
- PMCID: PMC3230792
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03499.x
Insights into the initiation of type 2 immune responses
Abstract
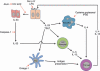
Type 2 immune responses, characterized by the differentiation of CD4+ T helper type 2 (Th2) cells and the production of the type 2 cytokines interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-5, IL-9 and IL-13, are associated with parasitic helminth infections and inflammatory conditions such as asthma and allergies. Until recently the initiating factors associated with type 2 responses had been poorly understood. This review addresses the recent advances in identifying the diverse range of antigens/allergens associated with type 2 responses and the function, expression and sources of type-2-initiating cytokines (thymic stromal lymphopoietin, IL-25 and IL-33). We also discuss the latest findings regarding innate lymphoid cells, such as nuocytes, as early sources of type 2 cytokines and their importance in protective immunity to helminth infections. These developments represent major breakthroughs in our understanding of type 2 immunity, and highlight the increased complexity existing between the innate and adaptive arms of these responses. These additional steps in the type 2 immune pathway also offer potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
© 2011 Medical Research Council. Immunology © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- McKerrow JH, Caffrey C, Kelly B, Loke P, Sajid M. Proteases in parasitic diseases. Annu Rev Pathol. 2006;1:497–536. - PubMed
-
- Chambers L, Brown A, Pritchard DI, Sreedharan S, Brocklehurst K, Kalsheker NA. Enzymatically active papain preferentially induces an allergic response in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;253:837–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

