Structural and biophysical determinants of αβ T-cell antigen recognition
- PMID: 22044041
- PMCID: PMC3246648
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03515.x
Structural and biophysical determinants of αβ T-cell antigen recognition
Abstract
The molecular rules that govern MHC restriction, and allow T-cells to differentiate between peptides derived from healthy cells and those from diseased cells, remain poorly understood. Here we provide an overview of the structural constraints that enable the T-cell receptor (TCR) to discriminate between self and non-self peptides, and summarize studies that have attempted to correlate the biophysical parameters of TCR/peptide-major histocompatibility complex (pMHC) binding with T-cell activation. We further review how the antigenic origin of peptide epitopes affects TCR binding parameters and the 'quality' of a T-cell response. Understanding the principles that govern pMHC recognition by T-cells will unlock pathways to the rational development of immunotherapeutic approaches for the treatment of infectious disease, cancer and autoimmunity.
© 2011 The Authors. Immunology © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
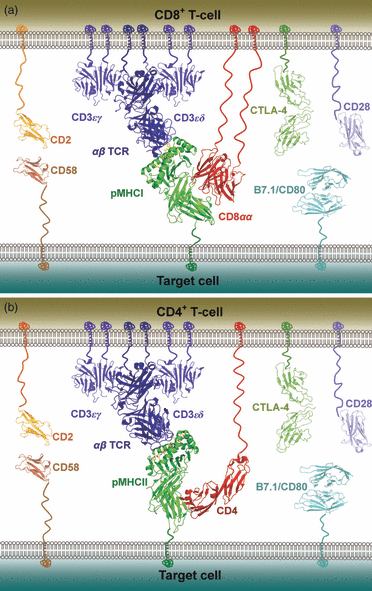

References
-
- Gao GF, Rao Z, Bell JI. Molecular coordination of αβ T-cell receptors and coreceptors CD8 and CD4 in their recognition of peptide-MHC ligands. Trends Immunol. 2002;23:408–13. - PubMed
-
- Janeway CA., Jr The T cell receptor as a multicomponent signalling machine: CD4/CD8 coreceptors and CD45 in T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:645–74. - PubMed
-
- Veillette A, Bookman MA, Horak EM, Bolen JB. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988;55:301–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

