Understanding the roles of basophils: breaking dawn
- PMID: 22044049
- PMCID: PMC3311041
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03530.x
Understanding the roles of basophils: breaking dawn
Abstract
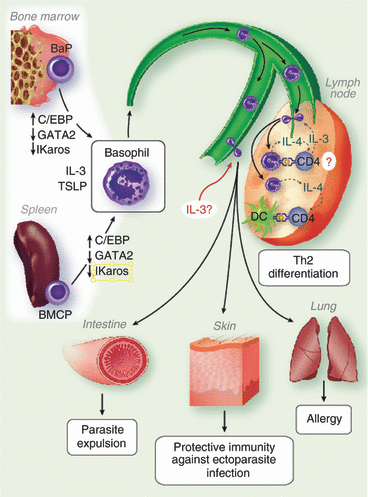
Early studies that used parasite-infected interleukin-4 (IL-4) reporter animals led us to identify basophils as the primary source of IL-4 and hence propose the hypothesis that basophils trigger the development of antigen-specific T helper type 2 (Th2) immune responses in vivo. These findings appeared to resolve a long-standing puzzle underlying Th2 immunity, that is, 'what is the source of the initial IL-4 necessary for CD4 T-cell differentiation into Th2 effector cells?'. However, results from extensive investigations of the contribution of basophils to Th2 immunity unveiled some controversial data that cast doubt on the initial hypothesis. In this review, the consensus and the controversy regarding the roles of basophils in infection and immunity, as well as outstanding questions for the future, are discussed.
Published 2011. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures
References
-
- Falcone FH, Zillikens D, Gibbs BF. The 21st century renaissance of the basophil? Current insights into its role in allergic responses and innate immunity. Exp Dermatol. 2006;15:855–64. - PubMed
-
- Ohnmacht C, Voehringer D. Basophil effector function and homeostasis during helminth infection. Blood. 2009;113:2816–25. - PubMed
-
- Ugajin T, Kojima T, Mukai K, et al. Basophils preferentially express mouse Mast Cell Protease 11 among the mast cell tryptase family in contrast to mast cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2009;86:1417–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

