Interleukin-23: as a drug target for autoimmune inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 22044352
- PMCID: PMC3277713
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03522.x
Interleukin-23: as a drug target for autoimmune inflammatory diseases
Abstract
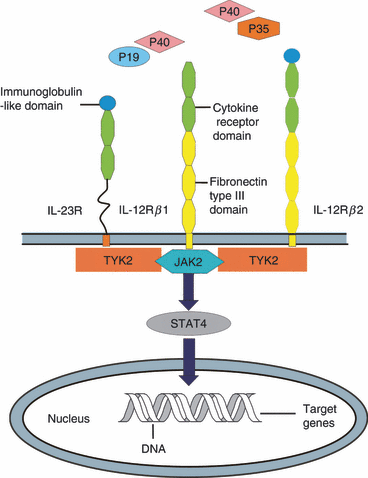
Interleukin-23 (IL-23) is a member of the IL-12 family of cytokines with pro-inflammatory properties. Its ability to potently enhance the expansion of T helper type 17 (Th17) cells indicates the responsibility for many of the inflammatory autoimmune responses. Emerging data demonstrate that IL-23 is a key participant in central regulation of the cellular mechanisms involved in inflammation. Both IL-23 and IL-17 form a new axis through Th17 cells, which has evolved in response to human diseases associated with immunoactivation and immunopathogeny, including bacterial or viral infections and chronic inflammation. Targeting of IL-23 or the IL-23 receptor or IL-23 axis is a potential therapeutic approach for autoimmune diseases including psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. The current review focuses on the immunobiology of IL-23 and summarizes the most recent findings on the role of IL-23 in the pre-clinical and ongoing clinical studies.
© 2011 The Authors. Immunology © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Kleinschek MA, Muller U, Brodie SJ, et al. IL-23 enhances the inflammatory cell response in Cryptococcus neoformans infection and induces a cytokine pattern distinct from IL-12. J Immunol. 2006;176:1098–106. - PubMed
-
- McKenzie BS, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ. Understanding the IL-23/IL-17 immune pathway. Trends Immunol. 2006;27:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, et al. Novel p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12. Immunity. 2000;13:715–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

