"Targeted disruption of the epithelial-barrier by Helicobacter pylori"
- PMID: 22044698
- PMCID: PMC3225297
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-811X-9-29
"Targeted disruption of the epithelial-barrier by Helicobacter pylori"
Abstract
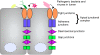
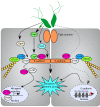
Helicobacter pylori colonizes the human gastric epithelium and induces chronic gastritis, which can lead to gastric cancer. Through cell-cell contacts the gastric epithelium forms a barrier to protect underlying tissue from pathogenic bacteria; however, H. pylori have evolved numerous strategies to perturb the integrity of the gastric barrier. In this review, we summarize recent research into the mechanisms through which H. pylori disrupts intercellular junctions and disrupts the gastric epithelial barrier.
Figures

References
-
- Peek RM Jr, Blaser MJ. Helicobacter pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:28–37. - PubMed
-
- Peek RM Jr, Crabtree JE. Helicobacter infection and gastric neoplasia. J Pathol. 2006;208:233–248. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

