Does N ratio affect survival in D1 and D2 lymph node dissection for gastric cancer?
- PMID: 22046089
- PMCID: PMC3199559
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i35.4007
Does N ratio affect survival in D1 and D2 lymph node dissection for gastric cancer?
Abstract
Aim: To identify whether there could have been changes in survival if lymph node ratio (N ratio) had been used.
Methods: We assessed 334 gastric adenocarcinoma cases retrospectively between 2001 and 2009. Two hundred and sixteen patients out of 334 were included in the study. Patients were grouped according to disection1 (D1) or dissection 2 (D2) dissection. We compared the estimated survival and actual survival determined by Pathologic nodes (pN) class and N ratio, and SPSS 15.0 software was used for statistical analysis.
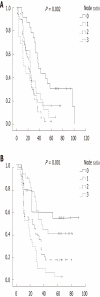
Results: Ninety-six (44.4%) patients underwent D1 dissection and 120 (55.6%) had D2 dissection. When groups were evaluated, 23 (24.0%) patients in D1 and 21 (17.5%) in D2 had stage migration (P = 0.001). When both D1 and D2 groups were evaluated for number of pathological lymph nodes, despite the fact that there was no difference in N ratio between D1 and D2 groups, a statistically significant difference was found between them with regard to pN1 and pN2 groups (P = 0.047, P = 0.044 respectively). In D1, pN0 had the longest survival while pN3 had the shortest. In D2, pN0 had the longest survival whereas pN3 had the shortest survival.
Conclusion: N ratio is an accurate staging system for defining prognosis and treatment plan, thus decreasing methodological errors in gastric cancer staging.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; Lymph node dissection; Node ratio; Tumor nodule metastasis.
Figures
References
-
- Greene FL. TNM staging for malignancies of the digestive tract: 2003 changes and beyond. Semin Surg Oncol. 2003;21:23–29. - PubMed
-
- Sayegh ME, Sano T, Dexter S, Katai H, Fukagawa T, Sasako M. TNM and Japanese staging systems for gastric cancer: how do they coexist? Gastric Cancer. 2004;7:140–148. - PubMed
-
- Bouvier AM, Haas O, Piard F, Roignot P, Bonithon-Kopp C, Faivre J. How many nodes must be examined to accurately stage gastric carcinomas? Results from a population based study. Cancer. 2002;94:2862–2866. - PubMed
-
- Coburn NG, Swallow CJ, Kiss A, Law C. Significant regional variation in adequacy of lymph node assessment and survival in gastric cancer. Cancer. 2006;107:2143–2151. - PubMed
-
- Mullaney PJ, Wadley MS, Hyde C, Wyatt J, Lawrence G, Hallissey MT, Fielding JW. Appraisal of compliance with the UICC/AJCC staging system in the staging of gastric cancer. Union Internacional Contra la Cancrum/American Joint Committee on Cancer. Br J Surg. 2002;89:1405–1408. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous