The SARS-coronavirus-host interactome: identification of cyclophilins as target for pan-coronavirus inhibitors
- PMID: 22046132
- PMCID: PMC3203193
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002331
The SARS-coronavirus-host interactome: identification of cyclophilins as target for pan-coronavirus inhibitors
Abstract
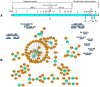
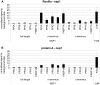
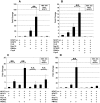
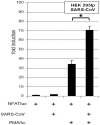
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are important human and animal pathogens that induce fatal respiratory, gastrointestinal and neurological disease. The outbreak of the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in 2002/2003 has demonstrated human vulnerability to (Coronavirus) CoV epidemics. Neither vaccines nor therapeutics are available against human and animal CoVs. Knowledge of host cell proteins that take part in pivotal virus-host interactions could define broad-spectrum antiviral targets. In this study, we used a systems biology approach employing a genome-wide yeast-two hybrid interaction screen to identify immunopilins (PPIA, PPIB, PPIH, PPIG, FKBP1A, FKBP1B) as interaction partners of the CoV non-structural protein 1 (Nsp1). These molecules modulate the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway that plays an important role in immune cell activation. Overexpression of NSP1 and infection with live SARS-CoV strongly increased signalling through the Calcineurin/NFAT pathway and enhanced the induction of interleukin 2, compatible with late-stage immunopathogenicity and long-term cytokine dysregulation as observed in severe SARS cases. Conversely, inhibition of cyclophilins by cyclosporine A (CspA) blocked the replication of CoVs of all genera, including SARS-CoV, human CoV-229E and -NL-63, feline CoV, as well as avian infectious bronchitis virus. Non-immunosuppressive derivatives of CspA might serve as broad-range CoV inhibitors applicable against emerging CoVs as well as ubiquitous pathogens of humans and livestock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

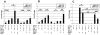
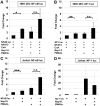
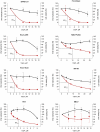
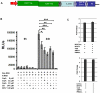
References
-
- Peiris JS, Yuen KY, Osterhaus AD, Stohr K. The severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2431–2441. - PubMed
-
- Drexler JF, Gloza-Rausch F, Glende J, Corman VM, Muth D, et al. Genomic characterization of severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus in European bats and classification of coronaviruses based on partial RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene sequences. J Virol. 2010;84:11336–11349. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Woo PC, Lau SK, Huang Y, Yuen KY. Coronavirus diversity, phylogeny and interspecies jumping. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2009;234:1117–1127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

