Differential Secondary Reconstitution of In Vivo-Selected Human SCID-Repopulating Cells in NOD/SCID versus NOD/SCID/γ chain Mice
- PMID: 22046557
- PMCID: PMC3200073
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/252953
Differential Secondary Reconstitution of In Vivo-Selected Human SCID-Repopulating Cells in NOD/SCID versus NOD/SCID/γ chain Mice
Abstract
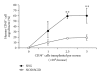
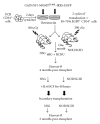
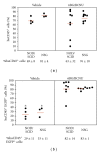
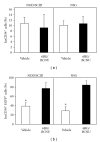
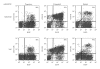
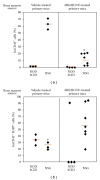
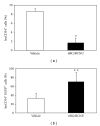
Humanized bone-marrow xenograft models that can monitor the long-term impact of gene-therapy strategies will help facilitate evaluation of clinical utility. The ability of the murine bone-marrow microenvironment in NOD/SCID versus NOD/SCID/γ chain(null) mice to support long-term engraftment of MGMT(P140K)-transduced human-hematopoietic cells following alkylator-mediated in vivo selection was investigated. Mice were transplanted with MGMT(P140K)-transduced CD34(+) cells and transduced cells selected in vivo. At 4 months after transplantation, levels of human-cell engraftment, and MGMT(P140K)-transduced cells in the bone marrow of NOD/SCID versus NSG mice varied slightly in vehicle- and drug-treated mice. In secondary transplants, although equal numbers of MGMT(P140K)-transduced human cells were transplanted, engraftment was significantly higher in NOD/SCID/γ chain(null) mice compared to NOD/SCID mice at 2 months after transplantation. These data indicate that reconstitution of NOD/SCID/γ chain(null) mice with human-hematopoietic cells represents a more promising model in which to test for genotoxicity and efficacy of strategies that focus on manipulation of long-term repopulating cells of human origin.
Figures

References
-
- Aiuti A, Slavin S, Aker M, et al. Correction of ADA-SCID by stem cell gene therapy combined with nonmyeloablative conditioning. Science. 2002;296(5577):2410–2413. - PubMed
-
- Aiuti A, Vai S, Mortellaro A, et al. Immune reconstitution in ADA-SCID after PBL gene therapy and discontinuation of enzyme replacement . Nature Medicine. 2002;8(5):423–425. - PubMed
-
- Cavazzana-Calvo M, Hacein-Bey S, de Saint-Basile G, Le Deist F, Fischer A. Gene therapy of severe combined immunodeficiencies. Transfusion Clinique et Biologique. 2000;7:259–260. - PubMed
-
- Cavazzana-Calvo M, Hacein-Bey S, De Saint Basile G, et al. Gene therapy of human severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)-X1 disease. Science. 2000;288(5466):669–672. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

