Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, beta (GADD45b)-mediated DNA demethylation in major psychosis
- PMID: 22048458
- PMCID: PMC3242315
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2011.221
Growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, beta (GADD45b)-mediated DNA demethylation in major psychosis
Erratum in
- Neuropsychopharmacology. 2012 Aug;37(9):2173
Abstract
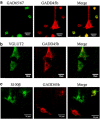
Aberrant neocortical DNA methylation has been suggested to be a pathophysiological contributor to psychotic disorders. Recently, a growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible, beta (GADD45b) protein-coordinated DNA demethylation pathway, utilizing cytidine deaminases and thymidine glycosylases, has been identified in the brain. We measured expression of several members of this pathway in parietal cortical samples from the Stanley Foundation Neuropathology Consortium (SFNC) cohort. We find an increase in GADD45b mRNA and protein in patients with psychosis. In immunohistochemistry experiments using samples from the Harvard Brain Tissue Resource Center, we report an increased number of GADD45b-stained cells in prefrontal cortical layers II, III, and V in psychotic patients. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor IX (BDNF IXabcd) was selected as a readout gene to determine the effects of GADD45b expression and promoter binding. We find that there is less GADD45b binding to the BDNF IXabcd promoter in psychotic subjects. Further, there is reduced BDNF IXabcd mRNA expression, and an increase in 5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine at its promoter. On the basis of these results, we conclude that GADD45b may be increased in psychosis compensatory to its inability to access gene promoter regions.
Figures

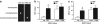
Similar articles
-
Role of Growth Arrest and DNA Damage-Inducible, Beta in Alcohol-Drinking Behaviors.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Feb;40(2):263-72. doi: 10.1111/acer.12965. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 26842245 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation/demethylation network expression in psychotic patients with a history of alcohol abuse.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013 Mar;37(3):417-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01947.x. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2013. PMID: 22958170 Clinical Trial.
-
Gadd45b and N-methyl-D-aspartate induced DNA demethylation in postmitotic neurons.Epigenomics. 2015;7(4):567-79. doi: 10.2217/epi.15.12. Epigenomics. 2015. PMID: 26111030 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Gadd45b in neurologic and neuropsychiatric disorders: An overview.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Oct 13;15:1021207. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.1021207. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36311022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active DNA demethylation in post-mitotic neurons: a reason for optimism.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:233-45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23958448 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neonatal Tactile Stimulation Alters Behaviors in Heterozygous Serotonin Transporter Male Rats: Role of the Amygdala.Front Behav Neurosci. 2020 Aug 12;14:142. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.00142. eCollection 2020. Front Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32903627 Free PMC article.
-
Gadd45b mediates depressive-like role through DNA demethylation.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 15;9(1):4615. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40844-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30874581 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal α-linolenic acid availability alters the expression of genes related to memory and to epigenetic machinery, and the Mecp2 DNA methylation in the whole brain of mouse offspring.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2014 Aug;36:38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2014.05.006. Epub 2014 May 24. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24866706 Free PMC article.
-
Huwe1 interacts with Gadd45b under oxygen-glucose deprivation and reperfusion injury in primary Rat cortical neuronal cells.Mol Brain. 2015 Dec 23;8:88. doi: 10.1186/s13041-015-0178-y. Mol Brain. 2015. PMID: 26698301 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics in the human brain.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Jan;38(1):183-97. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.78. Epub 2012 May 30. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 22643929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdolmaleky HM, Cheng KH, Russo A, Smith CL, Faraone SV, Wilcox M, et al. Hypermethylation of the reelin (RELN) promoter in the brain of schizophrenic patients: a preliminary report. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005;134B:60–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

