Neonatal Fc receptor and IgG-based therapeutics
- PMID: 22048693
- PMCID: PMC3225846
- DOI: 10.4161/mabs.3.5.16983
Neonatal Fc receptor and IgG-based therapeutics
Abstract
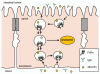
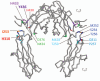
The majority of potent new biologics today are IgG-based molecules that have demonstrated tissue-targeting specificity with favorable clinical response. Several factors determine the efficacy of these products, including target specificity, serum half-life and effector functions via complement-dependent cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity or drug conjugates. In this review, we will focus on the interaction between therapeutic antibody and neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), which is one of the critical factors in determining the circulating antibody half-life. Specifically, we will review the fundamental biology of FcRn, FcRn functions in various organs, Fc mutations designed to modulate binding to FcRn, IgG-based therapeutics that directly exploit FcRn functions and tools and strategies used to study FcRn-IgG interactions. Comprehensive understanding of FcRn-IgG interactions not only allows for development of effective therapeutics, but also avoidance of potential adverse effects.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
