Regioselective glucosidation of trans-resveratrol in Escherichia coli expressing glucosyltransferase from Phytolacca americana
- PMID: 22048846
- PMCID: PMC3271224
- DOI: 10.1007/s10529-011-0784-4
Regioselective glucosidation of trans-resveratrol in Escherichia coli expressing glucosyltransferase from Phytolacca americana
Abstract
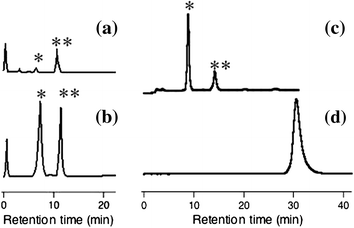
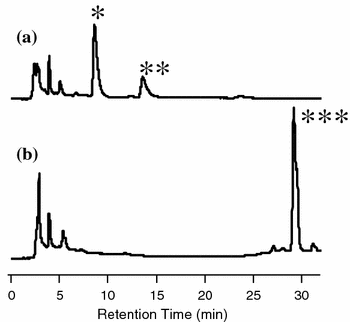
A glucosyltransferase (GT) of Phytolacca americana (PaGT3) was expressed in Escherichia coli and purified for the synthesis of two O-β-glucoside products of trans-resveratrol. The reaction was moderately regioselective with a ratio of 4'-O-β-glucoside: 3-O-β-glucoside at 10:3. We used not only the purified enzyme but also the E. coli cells containing the PaGT3 gene for the synthesis of glycoconjugates. E. coli cell cultures also have other advantages, such as a shorter incubation time compared with cultured plant cells, no need for the addition of exogenous glucosyl donor compounds such as UDP-glucose, and almost complete conversion of the aglycone to the glucoside products. Furthermore, a homology model of PaGT3 and mutagenesis studies suggested that His-20 would be a catalytically important residue.
Figures


References
-
- Furuya T, Ushiyama M, Asada Y, Yoshikawa T. Biotransformation of 2-phenylpropionic acid in root culture of Panax ginseng. Phytochemistry. 1989;28:483–487. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(89)80036-6. - DOI
-
- Hamada H, Ohiwa S, Nishida T, Katsuragi H, Takeda T, Hamada H, Nakajima N, Ishihara K, Hamada H, Hirata T, Nakajima N. One-step glucosylation of capsaicinoide by cultured cells of Phytolacca americana. Plant Biotechnol. 2003;20:253–255. doi: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.20.253. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

