Increased tryptophan transport in epileptogenic dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors
- PMID: 22048879
- PMCID: PMC3296904
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-011-0750-y
Increased tryptophan transport in epileptogenic dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors
Abstract
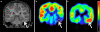
Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors (DNTs) are typically hypometabolic but can show increased amino acid uptake on positron emission tomography (PET). To better understand mechanisms of amino acid accumulation in epileptogenic DNTs, we combined quantitative α-[(11)C]methyl-L: -tryptophan (AMT) PET with tumor immunohistochemistry. Standardized uptake values (SUVs) of AMT and glucose were measured in 11 children with temporal lobe DNT. Additional quantification for AMT transport and metabolism was performed in 9 DNTs. Tumor specimens were immunostained for the L: -type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), a key enzyme of the immunomodulatory kynurenine pathway. All 11 tumors showed glucose hypometabolism, while mean AMT SUVs were higher than normal cortex in eight DNTs. Further quantification showed increased AMT transport in seven and high AMT metabolic rates in three DNTs. Two patients showing extratumoral cortical increases of AMT SUV had persistent seizures despite complete tumor resection. Resected DNTs showed moderate to strong LAT1 and mild to moderate IDO immunoreactivity, with the strongest expression in tumor vessels. These results indicate that accumulation of tryptophan in DNTs is driven by high amino acid transport, mediated by LAT1, which can provide the substrate for tumoral tryptophan metabolism through the kynurenine pathway, that can produce epileptogenic metabolites. Increased AMT uptake can extend to extratumoral cortex, and presence of such cortical regions may increase the likelihood of recurrent seizures following surgical excision of DNTs.
Figures



References
-
- Daumas-Duport C, Scheithauer BW, Chodkiewicz JP, Laws ER, Jr, Vedrenne C. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor: a surgically curable tumor of young patients with intractable partial seizures. Report of thirty-nine cases. Neurosurgery. 1988;23:545–556. - PubMed
-
- Daumas-Duport C. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumours. Brain Pathol. 1993;3:283–295. - PubMed
-
- Raymond AA, Halpin SF, Alsanjari N, et al. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor. Features in 16 patients. Brain. 1994;117(Pt 3):461–475. - PubMed
-
- Sharma MC, Jain D, Gupta A, et al. Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor: a clinicopathological study of 32 cases. Neurosurg Rev. 2009;32:161–169. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan AM, Lawson MA, Spataro J, et al. Positron emission tomography using [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose and [11C] l-methionine to metabolically characterize dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors. J Child Neurol. 1999;14:673–677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

