PKCδ-dependent activation of ERK1/2 leads to upregulation of the human NHE2 transcriptional activity in intestinal epithelial cell line C2BBe1
- PMID: 22052014
- PMCID: PMC3287399
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00363.2011
PKCδ-dependent activation of ERK1/2 leads to upregulation of the human NHE2 transcriptional activity in intestinal epithelial cell line C2BBe1
Abstract
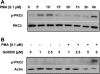
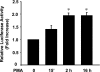
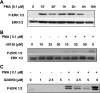
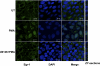
The apical Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE) isoform NHE2 is involved in transepithelial Na+ absorption in the intestine. Our earlier studies have shown that mitogenic agent phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) induces the expression of NHE2 through activation of transcription factor early growth response-1 (Egr-1) and its interactions with the NHE2 promoter. However, the signaling pathways involved in transcriptional stimulation of NHE2 in response to PMA in the intestinal epithelial cells are not known. Chemical inhibitors and genetic approaches were used to investigate the signaling pathways responsible for the stimulation of NHE2 expression by PMA via Egr-1 induction. We show that, in response to PMA, PKCδ, a member of novel PKC isozymes, and MEK-ERK1/2 pathway of mitogen-activated protein kinases stimulate the NHE2 expression in C2BBe1 intestinal epithelial cells. PMA rapidly and transiently induced activation of PKCδ. Small inhibitory RNA-mediated knockdown of PKCδ blocked the stimulatory effect of PMA on the NHE2 promoter activity. In addition, blockade of PKCδ by rottlerin, a PKCδ-specific inhibitor, and ERK1/2 by U0126, a MEK-ERK inhibitor, abrogated PMA-induced Egr-1 expression. Immunofluorescence studies revealed that inhibition of ERK1/2 activation prevents translocation of PMA-induced Egr-1 into the nucleus. Consistent with these data, PMA-induced Egr-1 interaction with the NHE2 promoter region was prevented in nuclear extracts from U0126-pretreated cells. In conclusion, our data provide the first evidence that the stimulatory effect of PMA on NHE2 expression is mediated through the initial activation of PKCδ, subsequent PKCδ-dependent activation of MEK-ERK1/2 signaling pathway, and stimulation of Egr-1 expression. Furthermore, we show that transcription factor Egr-1 acts as an intermediate effector molecule that links the upstream signaling cues to the long-term stimulation of NHE2 expression by PMA in C2BBe1 cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Transcriptional stimulation of the human NHE3 promoter activity by PMA: PKC independence and involvement of the transcription factor EGR-1.Biochem J. 2006 Jun 1;396(2):327-36. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051391. Biochem J. 2006. PMID: 16464174 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc finger transcription factor Egr-1 is involved in stimulation of NHE2 gene expression by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005 Oct;289(4):G653-63. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00010.2005. Epub 2005 Jun 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15976391
-
Extracellular acidosis stimulates NHE2 expression through activation of transcription factor Egr-1 in the intestinal epithelial cells.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 23;8(12):e82023. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082023. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376510 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic and acquired resistance to MEK1/2 inhibitors in cancer.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Aug;42(4):776-83. doi: 10.1042/BST20140129. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25109957 Review.
-
How ERK1/2 activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is subcellular localization the answer?Cell Cycle. 2009 Apr 15;8(8):1168-75. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.8.8147. Epub 2009 Apr 11. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19282669 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trefoil factor 2 activation of CXCR4 requires calcium mobilization to drive epithelial repair in gastric organoids.J Physiol. 2019 May;597(10):2673-2690. doi: 10.1113/JP277259. Epub 2019 Apr 14. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30912855 Free PMC article.
-
Isoform-specific phosphorylation-dependent regulation of connexin hemichannels.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Nov;114(5):3014-22. doi: 10.1152/jn.00575.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 23. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26400258 Free PMC article.
-
Role of early growth response 1 in inflammation-associated lung diseases.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2023 Aug 1;325(2):L143-L154. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00413.2022. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37401387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α regulates the expression of intestinal epithelial Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 3.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;314(1):G14-G21. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00225.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 7. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28882825 Free PMC article.
-
Apelin/Elabela-APJ: a novel therapeutic target in the cardiovascular system.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Mar;8(5):243. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.02.07. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32309390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Latif MM, Windle HJ, Davies A, Volkov Y, Kelleher D. A new mechanism of gastric epithelial injury induced by acid exposure: the role of Egr-1 and ERK signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem 108: 249–260, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Aggeli IK, Beis I, Gaitanaki C. ERKs and JNKs mediate hydrogen peroxide-induced Egr-1 expression and nuclear accumulation in H9c2 cells. Physiol Res 59: 443–454, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Amin MR, Malakooti J, Sandoval R, Dudeja PK, Ramaswamy K. IFN-γ and TNF-α regulate the human NHE3 gene expression by modulating the Sp family transcription factors in human intestinal epithelial cell line, C2BBe1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 291: C887–C896, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

