Immune profile of pediatric renal transplant recipients following alemtuzumab induction
- PMID: 22052056
- PMCID: PMC3269923
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2011040360
Immune profile of pediatric renal transplant recipients following alemtuzumab induction
Abstract
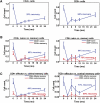
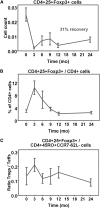
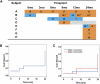
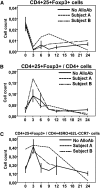
The incidence of developing circulating anti-human leukocyte antigen antibodies and the kinetics of T cell depletion and recovery among pediatric renal transplant recipients who receive alemtuzumab induction therapy are unknown. In a collaborative endeavor to minimize maintenance immunosuppression in pediatric renal transplant recipients, we enrolled 35 participants from four centers and treated them with alemtuzumab induction therapy and a steroid-free, calcineurin-inhibitor-withdrawal maintenance regimen. At 3 months after transplant, there was greater depletion of CD4(+) than CD8(+) T cells within the total, naive, memory, and effector memory subsets, although depletion of the central memory subset was similar for CD4(+) and CD8(+) cells. Although CD8(+) T cells recovered faster than CD4(+) subsets overall, they failed to return to pretransplant levels by 24 months after transplant. There was no evidence for greater recovery of either CD4(+) or CD8(+) memory cells than naïve cells. Alemtuzumab relatively spared CD4(+)CD25(+)FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells, resulting in a rise in their numbers relative to total CD4(+) cells and a ratio that remained at least at pretransplant levels throughout the study period. Seven participants (20%) developed anti-human leukocyte antigen antibodies without adversely affecting allograft function or histology on 2-year biopsies. Long-term follow-up is underway to assess the potential benefits of this regimen in children.
Figures


References
-
- Pearl JP, Parris J, Hale DA, Hoffmann SC, Bernstein WB, McCoy KL, Swanson SJ, Mannon RB, Roederer M, Kirk AD: Immunocompetent T-cells with a memory-like phenotype are the dominant cell type following antibody-mediated T-cell depletion. Am J Transplant 5: 465–474, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Trzonkowski P, Zilvetti M, Chapman S, Wieckiewicz J, Sutherland A, Friend P, Wood KJ: Homeostatic repopulation by CD28-CD8+ T cells in alemtuzumab-depleted kidney transplant recipients treated with reduced immunosuppression. Am J Transplant 8: 338–347, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Ciancio G, Burke GW, 3rd: Alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) in kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 8: 15–20, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Gallon L, Gagliardini E, Benigni A, Kaufman D, Waheed A, Noris M, Remuzzi G: Immunophenotypic analysis of cellular infiltrate of renal allograft biopsies in patients with acute rejection after induction with alemtuzumab (Campath-1H). Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1: 539–545, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Noris M, Casiraghi F, Todeschini M, Cravedi P, Cugini D, Monteferrante G, Aiello S, Cassis L, Gotti E, Gaspari F, Cattaneo D, Perico N, Remuzzi G: Regulatory T cells and T cell depletion: Role of immunosuppressive drugs. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 1007–1018, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

