Cortical parcellations of the macaque monkey analyzed on surface-based atlases
- PMID: 22052704
- PMCID: PMC3500860
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhr290
Cortical parcellations of the macaque monkey analyzed on surface-based atlases
Abstract
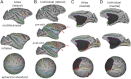
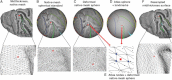
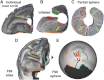
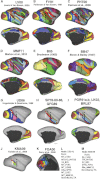
Surface-based atlases provide a valuable way to analyze and visualize the functional organization of cerebral cortex. Surface-based registration (SBR) is a primary method for aligning individual hemispheres to a surface-based atlas. We used landmark-constrained SBR to register many published parcellation schemes to the macaque F99 surface-based atlas. This enables objective comparison of both similarities and differences across parcellations. Cortical areas in the macaque vary in surface area by more than 2 orders of magnitude. Based on a composite parcellation derived from 3 major sources, the total number of macaque neocortical and transitional cortical areas is estimated to be about 130-140 in each hemisphere.
Figures


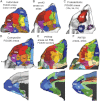
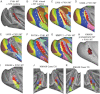
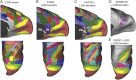
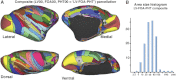
References
-
- Black KJ, Koller JM, Snyder AZ, Perlmutter JS. Template images for nonhuman primate neuroimaging: 2. Macaque. Neuroimage. 2001;14:744–748. - PubMed
-
- Brodmann K. Beitraege zur histologischen Lokalisation der Grosshirnrinde: dritte Mitteilung: Die Rindenfelder der niederen Affen Journal fuer Psychologie und Neurologie. Neuroimage. 1905;4:5/6:177–226.
-
- Carmichael ST, Price JL. Architectonic subdivision of the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex in the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1994;346:366–402. - PubMed
-
- Carmichael ST, Price JL. Connectional networks within the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex of macaque monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1996;371:179–207. - PubMed

