Maternal diesel inhalation increases airway hyperreactivity in ozone-exposed offspring
- PMID: 22052876
- PMCID: PMC3359947
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0256OC
Maternal diesel inhalation increases airway hyperreactivity in ozone-exposed offspring
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Maternal diesel inhalation increases airway hyperreactivity in ozone-exposed offspring.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;52(4):523. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.524retraction. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25830632 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
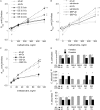
Air pollutant exposure is linked with childhood asthma incidence and exacerbations, and maternal exposure to airborne pollutants during pregnancy increases airway hyperreactivity (AHR) in offspring. To determine if exposure to diesel exhaust (DE) during pregnancy worsened postnatal ozone-induced AHR, timed pregnant C57BL/6 mice were exposed to DE (0.5 or 2.0 mg/m(3)) 4 hours daily from Gestation Day 9-17, or received twice-weekly oropharyngeal aspirations of the collected DE particles (DEPs). Placentas and fetal lungs were harvested on Gestation Day 18 for cytokine analysis. In other litters, pups born to dams exposed to air or DE, or to dams treated with aspirated diesel particles, were exposed to filtered air or 1 ppm ozone beginning the day after birth, for 3 hours per day, 3 days per week for 4 weeks. Additional pups were monitored after a 4-week recovery period. Diesel inhalation or aspiration during pregnancy increased levels of placental and fetal lung cytokines. There were no significant effects on airway leukocytes, but prenatal diesel augmented ozone-induced elevations of bronchoalveolar lavage cytokines at 4 weeks. Mice born to the high-concentration diesel-exposed dams had worse ozone-induced AHR, which persisted in the 4-week recovery animals. Prenatal diesel exposure combined with postnatal ozone exposure also worsened secondary alveolar crest development. We conclude that maternal inhalation of DE in pregnancy provokes a fetal inflammatory response that, combined with postnatal ozone exposure, impairs alveolar development, and causes a more severe and long-lasting AHR to ozone exposure.
Figures



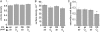
Comment in
-
Findings of Research Misconduct.Fed Regist. 2019 Nov 7;84(216):60097-60098. Fed Regist. 2019. PMID: 37547121 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hertz-Picciotto I, Park HY, Dostal M, Kocan A, Trnovec T, Sram R. Prenatal exposures to persistent and non-persistent organic compounds and effects on immune system development. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2008;102:146–154 - PubMed
-
- Margolis HG, Mann JK, Lurmann FW, Mortimer KM, Balmes JR, Hammond SK, Tager IB. Altered pulmonary function in children with asthma associated with highway traffic near residence. Int J Environ Health Res 2009;19:139–155 - PubMed
-
- Fedulov AV, Kobzik L. Immunotoxicologic analysis of maternal transmission of asthma risk. J Immunotoxicol 2008;5:445–452 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

