Involvement of ceramide in cell death responses in the pulmonary circulation
- PMID: 22052925
- PMCID: PMC3359077
- DOI: 10.1513/pats.201104-034MW
Involvement of ceramide in cell death responses in the pulmonary circulation
Abstract
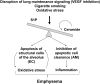
Ceramides are signaling sphingolipids involved in cellular homeostasis but also in pathological processes such as unwanted apoptosis, growth arrest, oxidative stress, or senescence. Several enzymatic pathways are responsible for the synthesis of ceramides, which can be activated in response to exogenous stimuli such as cytokines, radiation, or oxidative stress. Endothelial cells are particularly rich in acid sphingomyelinases, which can be rapidly activated to produce ceramides, both intracellular and at the plasma membrane. In addition, neutral sphingomyelinases, the de novo pathway and the ceramide recycling pathway, may generate excessive ceramides involved in endothelial cell responses. When up-regulated, ceramides trigger signaling pathways that culminate in endothelial cell death, which in murine lungs has been linked to the development of emphysema-like disease. Furthermore, ceramides may be released paracellularly where they are believed to exert paracrine activities. Such effects, along with ceramides released by inflammatory mediators, may contribute to lung inflammation and pulmonary edema, because ceramide-challenged pulmonary endothelial cells exhibit decreased barrier function, independent of apoptosis. Reestablishing the sphingolipid homeostasis, either by modulating ceramide synthesis or by opposing its biological effects through augmentation of the prosurvival sphingosine-1 phosphate, may alleviate acute or chronic pulmonary conditions characterized by vascular endothelial cell death or dysfunction.
Figures

References
-
- Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008;9:139–150 - PubMed
-
- Pettus BJ, Chalfant CE, Hannun YA. Ceramide in apoptosis: an overview and current perspectives. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002;1585:114–125 - PubMed
-
- Uhlig S, Gulbins E. Sphingolipids in the lungs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008;178:1100–1114 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
