Blocking NF-κB: an inflammatory issue
- PMID: 22052926
- PMCID: PMC3359076
- DOI: 10.1513/pats.201101-009MW
Blocking NF-κB: an inflammatory issue
Abstract
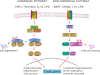
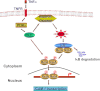
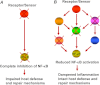
The nuclear factor (NF)-κB is considered the master regulator of inflammatory responses. Studies in mouse models have established this transcription factor as an important mediator of many inflammatory disease states, including pulmonary diseases such as acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Endothelial cells provide the first barrier for leukocytes migrating to the inflamed sites and hence offer an attractive cellular context for targeting NF-κB for treatment of these diseases. However, recent studies showing that NF-κB also plays an important role in resolution phase of inflammation and in tissue repair and homeostasis have challenged the view of therapeutic inhibition of NF-κB. This article reviews the regulation of NF-κB in the context of endothelial cell signaling and provides a perspective on why "dampening" rather than "abolishing" NF-κB activation may be a safe and effective treatment strategy for inflammation-associated pulmonary and other inflammatory diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 2000;342:1334–1349 - PubMed
-
- Maniatis NA, Orfanos SE. The endothelium in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care 2008;14:22–30 - PubMed
-
- Goodman RB, Strieter RM, Martin DP, Steinberg KP, Milberg JA, Maunder RJ, Kunkel SL, Walz A, Hudson LD, Martin TR. Inflammatory cytokines in patients with persistence of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996;154:602–611 - PubMed
-
- Fan J, Ye RD, Malik AB. Transcriptional mechanisms of acute lung injury. Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2001;281:L1037–L1050 - PubMed
-
- Springer TA. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell 1994;76:301–314 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
