Early skeletal and biochemical alterations in pediatric chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 22052943
- PMCID: PMC3265337
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.05940611
Early skeletal and biochemical alterations in pediatric chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background and objectives: The relationship between parathyroid hormone, fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23), and indices of bone turnover and mineralization in children with early CKD is unknown; thus, this study characterizes the features of renal osteodystrophy and their relationship to biochemical markers of mineral metabolism.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Fifty-two patients 2-21 years of age with predialysis CKD underwent tetracycline-labeled bone biopsy. Anthropomorphic measurements and biochemical values were obtained at the time of biopsy.
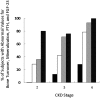
Results: Serum phosphorus levels were increased in 4% of patients with stage 3 CKD and 43% of those with stage 4/5 CKD. Parathyroid hormone concentrations were elevated in 36% of patients with stage 2, 71% with stage 3, and 93% with stage 4/5 CKD, whereas FGF-23 values were elevated in 81% of all patients, regardless of CKD stage. Bone turnover was normal in all patients with stage 2, but was increased in 13% with stage 3 and 29% with stage 4/5 CKD. Defective mineralization was present in 29% of patients with stage 2, 42% with stage 3, and 79% with stage 4/5 CKD. Defective skeletal mineralization was associated with lower serum calcium levels and increased parathyroid hormone concentrations.
Conclusions: Elevated circulating FGF-23 levels and defects in skeletal mineralization early in the course of CKD suggest that factors other than the traditional markers of mineral deficiency play a crucial role in the development of renal bone disease.
Figures
References
-
- North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study (NAPRTCS): Annual Report, 2005
-
- Klaus G, Watson A, Edefonti A, Fischbach M, Rönnholm K, Schaefer F, Simkova E, Stefanidis CJ, Strazdins V, Vande Walle J, Schröder C, Zurowska A, Ekim M. European Pediatric Dialysis Working Group (EPDWG): Prevention and treatment of renal osteodystrophy in children on chronic renal failure: European guidelines. Pediatr Nephrol 21: 151–159, 2006 - PMC - PubMed
-
- National Kidney Foundation: K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for bone metabolism and disease in children with chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis 46: S1–S121, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Waller S, Ledermann S, Trompeter R, van’t Hoff W, Ridout D, Rees L: Catch-up growth with normal parathyroid hormone levels in chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 18: 1236–1241, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Schmitt CP, Ardissino G, Testa S, Claris-Appiani A, Mehls O: Growth in children with chronic renal failure on intermittent versus daily calcitriol. Pediatr Nephrol 18: 440–444, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K23 DK080984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-073039/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK035423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- DK-67563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-51081/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073039/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR-00865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK-35423/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK051081/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033176/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

