Autophagy proteins regulate the secretory component of osteoclastic bone resorption
- PMID: 22055344
- PMCID: PMC3244473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.016
Autophagy proteins regulate the secretory component of osteoclastic bone resorption
Erratum in
- Dev Cell. 2011 Dec 13;21(6):1179
Abstract
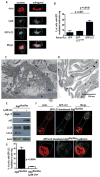
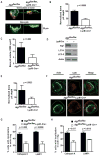
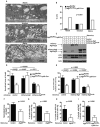
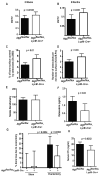
Osteoclasts resorb bone via the ruffled border, whose complex folds are generated by secretory lysosome fusion with bone-apposed plasma membrane. Lysosomal fusion with the plasmalemma results in acidification of the resorptive microenvironment and release of CatK to digest the organic matrix of bone. The means by which secretory lysosomes are directed to fuse with the ruffled border are enigmatic. We show that proteins essential for autophagy, including Atg5, Atg7, Atg4B, and LC3, are important for generating the osteoclast ruffled border, the secretory function of osteoclasts, and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo. Further, Rab7, which is required for osteoclast function, localizes to the ruffled border in an Atg5-dependent manner. Thus, autophagy proteins participate in polarized secretion of lysosomal contents into the extracellular space by directing lysosomes to fuse with the plasma membrane. These findings are in keeping with a putative link between autophagy genes and human skeletal homeostasis.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Autophagic factors cut to the bone.Dev Cell. 2011 Nov 15;21(5):808-10. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.10.021. Dev Cell. 2011. PMID: 22075143
References
-
- Cann GM, Guignabert C, Ying L, Deshpande N, Bekker JM, Wang L, Zhou B, Rabinovitch M. Developmental expression of LC3alpha and beta: absence of fibronectin or autophagy phenotype in LC3beta knockout mice. Dev Dyn. 2008;237:187–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI084887/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR032788/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR046523/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AR046523/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI0848887/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR054618/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR057235/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR057037/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR032788/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057160/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR057235/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR054618/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 AG032795/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR023660/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AR046523/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG032795/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR057037/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

