Primary human cervical carcinoma cells require human papillomavirus E6 and E7 expression for ongoing proliferation
- PMID: 22056390
- PMCID: PMC3229657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.10.012
Primary human cervical carcinoma cells require human papillomavirus E6 and E7 expression for ongoing proliferation
Abstract
Repression of human papillomavirus (HPV) E6 and E7 oncogenes in established cervical carcinoma cell lines causes senescence due to reactivation of cellular tumor suppressor pathways. Here, we determined whether ongoing expression of HPV16 or HPV18 oncogenes is required for the proliferation of primary human cervical carcinoma cells in serum-free conditions at low passage number after isolation from patients. We used an SV40 viral vector expressing the bovine papillomavirus E2 protein to repress E6 and E7 in these cells. To enable efficient SV40 infection and E2 gene delivery, we first incubated the primary cervical cancer cells with the ganglioside GM1, a cell-surface receptor for SV40 that is limiting in these cells. Repression of HPV in primary cervical carcinoma cells caused them to undergo senescence, but the E2 protein had little effect on HPV-negative primary cells. These data suggest that E6 and E7 dependence is an inherent property of human cervical cancer cells.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures









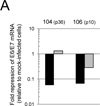

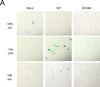

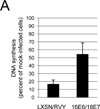

References
-
- Balmain A, Harris CC. Carcinogenesis in mouse and human cells: parallels and paradoxes. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21(3):371–377. - PubMed
-
- Bignotti E, Tassi RA, Calza S, Ravaggi A, Romani C, Rossi E, Falchetti M, Odicino FE, Pecorelli S, Santin AD. Differential gene expression profiles between tumor biopsies and short-term primary cultures of ovarian serous carcinomas: identification of novel molecular biomarkers for early diagnosis and therapy. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;103(2):405–416. - PubMed

