Splitting the task: Ubp8 and Ubp10 deubiquitinate different cellular pools of H2BK123
- PMID: 22056669
- PMCID: PMC3219228
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.177220.111
Splitting the task: Ubp8 and Ubp10 deubiquitinate different cellular pools of H2BK123
Abstract
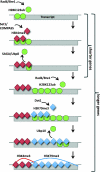
Monoubiquitination of H2BK123 (H2BK123ub), catalyzed by Rad6/Bre1, is a transient histone modification with roles in transcription and is essential for establishing H3K4 and H3K79 trimethylations (H3K4me3 and H3K79me3). Here, we investigated the chromatin network around H2BK123ub by examining its localization and co-occurrence with its dependent marks as well as the transcription elongation mark H3K36me3 across the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In yeast, H2BK123ub is removed by the deubiquitinases Ubp8 and Ubp10, but their genomic target regions remain to be determined. Genome-wide maps of H2BK123ub in the absence of Ubp8 and Ubp10 revealed their distinct target loci, which were genomic sites enriched for H3K4me3 and H3K79me3, respectively. We propose an extended model of the H2BK123ub cross-talk by integrating existing relationships with the substrate specificities of Ubp8 and Ubp10 reported here.
Figures

References
-
- Daniel JA, Torok MS, Sun Z-W, Schieltz D, Allis CD, Yates JR, Grant PA 2004. Deubiquitination of histone H2B by a yeast acetyltransferase complex regulates transcription. J Biol Chem 279: 1867–1871 - PubMed
-
- Dover J, Schneider J, Tawiah-Boateng M, Wood A, Dean K, Johnston M, Shilatifard A 2002. Methylation of histone H3 by COMPASS requires ubiquitination of histone H2B by Rad6. J Biol Chem 277: 28368–28371 - PubMed
-
- Droit A, Cheung C, Gottardo R 2010. rMAT—an R/Bioconductor package for analyzing ChIP–chip experiments. Bioinformatics 26: 678–679 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
