Genome-wide function of H2B ubiquitylation in promoter and genic regions
- PMID: 22056671
- PMCID: PMC3219230
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.177238.111
Genome-wide function of H2B ubiquitylation in promoter and genic regions
Abstract
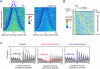
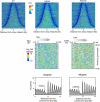
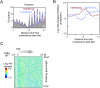
Nucleosomal organization in and around genes may contribute substantially to transcriptional regulation. The contribution of histone modifications to genome-wide nucleosomal organization has not been systematically evaluated. In the present study, we examine the role of H2BK123 ubiquitylation, a key regulator of several histone modifications, on nucleosomal organization at promoter, genic, and transcription termination regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Using high-resolution MNase chromatin immunoprecipitation and sequencing (ChIP-seq), we map nucleosome positioning and occupancy in mutants of the H2BK123 ubiquitylation pathway. We found that H2B ubiquitylation-mediated nucleosome formation and/or stability inhibits the assembly of the transcription machinery at normally quiescent promoters, whereas ubiquitylation within highly active gene bodies promotes transcription elongation. This regulation does not proceed through ubiquitylation-regulated histone marks at H3K4, K36, and K79. Our findings suggest that mechanistically similar functions of H2B ubiquitylation (nucleosome assembly) elicit different functional outcomes on genes depending on its positional context in promoters (repressive) versus transcribed regions (activating).
Figures



References
-
- Albert I, Mavrich TN, Tomsho LP, Qi J, Zanton SJ, Schuster SC, Pugh BF 2007. Translational and rotational settings of H2A.Z nucleosomes across the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 446: 572–576 - PubMed
-
- Belotserkovskaya R, Oh S, Bondarenko VA, Orphanides G, Studitsky VM, Reinberg D 2003. Fact facilitates transcription-dependent nucleosome alteration. Science 301: 1090–1093 - PubMed
-
- Carrozza MJ, Li B, Florens L, Suganuma T, Swanson SK, Lee KK, Shia WJ, Anderson S, Yates J, Washburn MP, et al. 2005. Histone H3 methylation by Set2 directs deacetylation of coding regions by Rpd3S to suppress spurious intragenic transcription. Cell 123: 581–592 - PubMed
-
- Celona B, Weiner A, Di Felice F, Mancuso FM, Cesarini E, Rossi RL, Gregory L, Baban D, Rossetti G, Grianti P, et al. 2011. Substantial histone reduction modulates genomewide nucleosomal occupancy and global transcriptional output. PLoS Biol 9: e1001086 doi: 10.1371/jounral.pbio.1001086 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
