The E3 ligase Itch and deubiquitinase Cyld act together to regulate Tak1 and inflammation
- PMID: 22057290
- PMCID: PMC3219826
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.2157
The E3 ligase Itch and deubiquitinase Cyld act together to regulate Tak1 and inflammation
Abstract
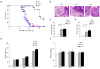
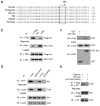
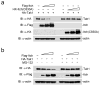
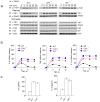
Chronic inflammation has been strongly associated with tumor progression, but the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Here we demonstrate that E3 ligase Itch and deubiquitinase Cyld formed a complex via interaction through 'WW-PPXY' motifs. The Itch-Cyld complex sequentially cleaved Lys63-linked ubiquitin chains and catalyzed Lys48-linked ubiquitination on the kinase Tak1 to terminate inflammatory signaling via tumor necrosis factor. Reconstitution of wild-type Cyld but not the mutant Cyld(Y485A), which cannot associate with Itch, blocked sustained Tak1 activation and proinflammatory cytokine production by Cyld(-/-) bone marrow-derived macrophages. Deficiency in Itch or Cyld led to chronic production of tumor-promoting cytokines by tumor-associated macrophages and aggressive growth of lung carcinoma. Thus, we have identified an Itch-Cyld-mediated regulatory mechanism in innate inflammatory cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
It takes two to tango: a new couple in the family of ubiquitin-editing complexes.Nat Immunol. 2011 Nov 16;12(12):1133-5. doi: 10.1038/ni.2165. Nat Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22089210 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

