Left ventricular remodeling in swine after myocardial infarction: a transcriptional genomics approach
- PMID: 22057716
- PMCID: PMC3228945
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-011-0229-1
Left ventricular remodeling in swine after myocardial infarction: a transcriptional genomics approach
Abstract
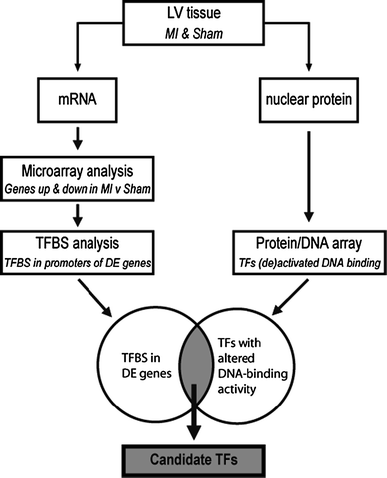
Despite the apparent appropriateness of left ventricular (LV) remodeling following myocardial infarction (MI), it poses an independent risk factor for development of heart failure. There is a paucity of studies into the molecular mechanisms of LV remodeling in large animal species. We took an unbiased molecular approach to identify candidate transcription factors (TFs) mediating the genetic reprogramming involved in post-MI LV remodeling in swine. Left ventricular tissue was collected from remote, non-infarcted myocardium, 3 weeks after MI-induction or sham-surgery. Microarray analysis identified 285 upregulated and 278 downregulated genes (FDR < 0.05). Of these differentially expressed genes, the promoter regions of the human homologs were searched for common TF binding sites (TFBS). Eighteen TFBS were overrepresented >two-fold (p < 0.01) in upregulated and 13 in downregulated genes. Left ventricular nuclear protein extracts were assayed for DNA-binding activity by protein/DNA array. Out of 345 DNA probes, 30 showed signal intensity changes >two-fold. Five TFs were identified in both TFBS and protein/DNA array analyses, which showed matching changes for COUP-TFII and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) only. Treatment of swine with the GR antagonist mifepristone after MI reduced the post-MI increase in LV mass, but LV dilation remained unaffected. Thus, using an unbiased approach to study post-MI LV remodeling in a physiologically relevant large animal model, we identified COUP-TFII and GR as potential key mediators of post-MI remodeling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene reprogramming in exercise-induced cardiac hypertrophy in swine: A transcriptional genomics approach.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Dec;77:168-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Oct 22. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25451387
-
Genetic basis for chamber-specific ventricular phenotypes in the rat infarct model.Cardiovasc Res. 2003 Feb;57(2):477-85. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(02)00703-4. Cardiovasc Res. 2003. PMID: 12566120
-
Apoptotic transcriptional profile remains activated in late remodeled left ventricle after myocardial infarction in swine infarcted hearts with preserved ejection fraction.Pharmacol Res. 2013 Apr;70(1):41-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.12.007. Epub 2013 Jan 4. Pharmacol Res. 2013. PMID: 23295943
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
-
The effects of different initiation time of exercise training on left ventricular remodeling and cardiopulmonary rehabilitation in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction.Disabil Rehabil. 2016;38(3):268-76. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2015.1036174. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Disabil Rehabil. 2016. PMID: 25885667 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying key genes associated with acute myocardial infarction.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Oct;96(42):e7741. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007741. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29049183 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of region specific gene expression patterns in the heart and systemic responses after experimental myocardial ischemia.Oncotarget. 2017 May 17;8(37):60809-60825. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17955. eCollection 2017 Sep 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28977827 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic carvedilol treatment partially reverses the right ventricular failure transcriptional profile in experimental pulmonary hypertension.Physiol Genomics. 2013 Jun 17;45(12):449-61. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00166.2012. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Physiol Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23632417 Free PMC article.
-
Corticosteroid Receptors in Cardiac Health and Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1390:109-122. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-11836-4_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36107315
-
New genetic variants associated with major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute coronary syndromes and treated with clopidogrel and aspirin.Pharmacogenomics J. 2021 Dec;21(6):664-672. doi: 10.1038/s41397-021-00245-5. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Pharmacogenomics J. 2021. PMID: 34158603 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brady JP, Kantorow M, Sax CM, Donovan DM, Piatigorsky J. Murine transcription factor alpha A-crystallin binding protein I. Complete sequence, gene structure, expression, and functional inhibition via antisense RNA. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:1221–1229. - PubMed
-
- Cadepond F, Ulmann A, Baulieu EE. RU486 (mifepristone): mechanisms of action and clinical uses. Annu Rev Med. 1997;48:129–156. - PubMed
-
- Chorianopoulos E, Heger T, Lutz M, Frank D, Bea F, Katus HA, Frey N. FGF-inducible 14-kDa protein (Fn14) is regulated via the RhoA/ROCK kinase pathway in cardiomyocytes and mediates nuclear factor-kappaB activation by TWEAK. Basic Res Cardiol. 2010;105:301–313. - PubMed
-
- Colbert MC, Hall DG, Kimball TR, Witt SA, Lorenz JN, Kirby ML, Hewett TE, Klevitsky R, Robbins J. Cardiac compartment-specific overexpression of a modified retinoic acid receptor produces dilated cardiomyopathy and congestive heart failure in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest. 1997;100:1958–1968. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Conraads VM, Vrints CJ, Rodrigus IE, Hoymans VY, Van Craenenbroeck EM, Bosmans J, Claeys MJ, Van Herck P, Linke A, Schuler G, Adams V. Depressed expression of MuRF1 and MAFbx in areas remote of recent myocardial infarction: a mechanism contributing to myocardial remodeling? Basic Res Cardiol. 2010;105:219–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

