The effects of vascular endothelial growth factor C knockdown in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 22057733
- PMCID: PMC11824638
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-011-1079-9
The effects of vascular endothelial growth factor C knockdown in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: We investigated the role of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) by knocking down VEGF-C expression in the ESCC cell line EC9706.
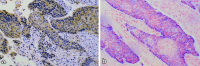
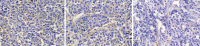
Methods: Immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization techniques were used to detect the expression of VEGF-C expression in ESCC tissues. We also investigated the relationship between VEGF-C expression and lymph node metastasis. We designed a siRNA expression plasmid for VEGF-C and transfected it into EC9706 cells. Stable clones were selected, and VEGF-C expression was analyzed by RT-PCR and western blotting. Cells were inoculated into nude mice. The expression of VEGF-C in the resulting tumors was analyzed by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization.
Results: VEGF-C is highly expressed in ESCC and correlated with lymph node metastasis, as high levels were observed in patients presenting with lymph node metastases relative to those who did not (P < 0.01). Transfection with VEGF-C-siRNA decreased the expression of VEGF-C mRNA and protein. ESCC cells stably transfected with VEGF-C-siRNA expressed very low levels of VEGF-C (P < 0.01 compared with control). This knockdown effect persisted when the cells were inoculated into nude mice and allowed to form tumors.
Conclusions: The siRNA-targeted knockdown of VEGF-C led to a significant reduction in VEGF-C expression. This siRNA technique could be used for gene therapy in ESCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

