Ricin and Shiga toxins: effects on host cell signal transduction
- PMID: 22057792
- PMCID: PMC7120278
- DOI: 10.1007/82_2011_181
Ricin and Shiga toxins: effects on host cell signal transduction
Abstract
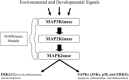
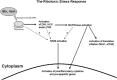
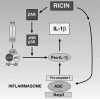
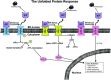
Shiga toxins and ricin are potent inhibitors of protein synthesis. In addition to causing inhibition of protein synthesis, these toxins activate proinflammatory signaling cascades that may contribute to the severe diseases associated with toxin exposure. Treatment of cells with Shiga toxins and ricin have been shown to activate a number of signaling pathways including those associated with the ribotoxic stress response, Nuclear factor kappa B activation, inflammasome activation, the unfolded protein response, mTOR signaling, hemostasis, and retrograde trafficking. In this chapter, we review our current understanding of these signaling pathways as they pertain to intoxication by Shiga toxins and ricin.
Figures
References
-
- Arab S, Lingwood CA. Intracellular targeting of the endoplasmic reticulum/nuclear envelope by retrograde transport may determine cell hypersensitivity to verotoxin via globotriaosyl ceramide fatty acid isoform traffic. J Cell Physiol. 1998;177:646–660. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199812)177:4<646::AID-JCP15>3.0.CO;2-B. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baenziger JU, Fiete D. Structural determinants of ricinus communis agglutinin and toxin specificity for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:9795–9799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

