Insulin receptor signaling mediates APP processing and β-amyloid accumulation without altering survival in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22057897
- PMCID: PMC3543743
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-011-9333-2
Insulin receptor signaling mediates APP processing and β-amyloid accumulation without altering survival in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
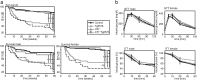
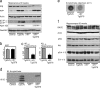
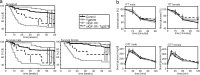
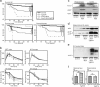
In brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD), expression of insulin receptor (IR), insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), and insulin receptor substrate proteins is downregulated. A key step in the pathogenesis of AD is the accumulation of amyloid precursor protein (APP) cleavage products, β-amyloid (Aβ)(1-42) and Aβ(1-40). Recently, we and others have shown that central IGF-1 resistance reduces Aβ accumulation as well as Aβ toxicity and promotes survival. To define the role of IR in this context, we crossed neuron-specific IR knockout mice (nIR(-/-)) with Tg2576 mice, a well-established mouse model of an AD-like pathology. Here, we show that neuronal IR deficiency in Tg2576 (nIR(-/-)Tg2576) mice leads to markedly decreased Aβ burden but does not rescue premature mortality of Tg2576 mice. Analyzing APP C-terminal fragments (CTF) revealed decreased α-/β-CTFs in the brains of nIR(-/-)Tg2576 mice suggesting decreased APP processing. Cell based experiments showed that inhibition of the PI3-kinase pathway suppresses endosomal APP cleavage and decreases α- as well as β-secretase activity. Deletion of only one copy of the neuronal IGF-1R partially rescues the premature mortality of Tg2576 mice without altering total amyloid load. Analysis of Tg2576 mice expressing either a dominant negative or constitutively active form of forkhead box-O (FoxO)1 did not reveal any alteration of amyloid burden, APP processing and did not rescue premature mortality in these mice. Thus, our findings identified IR signaling as a potent regulator of Aβ accumulation in vivo. But exclusively decreased IGF-1R expression reduces AD-associated mortality independent of β-amyloid accumulation and FoxO1-mediated transcription.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Neuronal IGF-1 resistance reduces Abeta accumulation and protects against premature death in a model of Alzheimer's disease.FASEB J. 2009 Oct;23(10):3315-24. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-132043. Epub 2009 Jun 1. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19487308
-
Amyloid precursor protein processing and retinal pathology in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009 Sep;247(9):1213-21. doi: 10.1007/s00417-009-1060-3. Epub 2009 Mar 7. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19271231
-
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor inhibition in transgenic Alzheimer-like Tg2576 mice by scopolamine favours the amyloidogenic route of processing of amyloid precursor protein.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2006 Apr-May;24(2-3):149-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2005.11.010. Epub 2006 Jan 19. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16423497
-
The role of IGF-1 receptor and insulin receptor signaling for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: from model organisms to human disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2009 Jun;6(3):213-23. doi: 10.2174/156720509788486527. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2009. PMID: 19519303 Review.
-
The role of neuronal insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: possible therapeutic implications.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014 Mar;13(2):322-37. doi: 10.2174/18715273113126660141. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 24059318 Review.
Cited by
-
FoxO3a is activated and executes neuron death via Bim in response to β-amyloid.Cell Death Dis. 2013 May 9;4(5):e625. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.148. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23661003 Free PMC article.
-
Body fluid biomarkers in Alzheimer's disease.Ann Transl Med. 2015 Apr;3(5):70. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.02.13. Ann Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25992369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential effects of diet- and genetically-induced brain insulin resistance on amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2019 Apr 12;14(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13024-019-0315-7. Mol Neurodegener. 2019. PMID: 30975165 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular hormetic response to 27-hydroxycholesterol promotes neuroprotection through AICD induction of MAST4 abundance and kinase activity.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 24;7(1):13898. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13933-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29066835 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of Candidate Gene Expression and Neuroprotection by Piperine in Streptozotocin-Induced Hyperglycemia and Memory Impairment in Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Mar 2;11:595471. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.595471. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33737876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belgardt BF, Husch A, Rother E, Ernst MB, Wunderlich FT, Hampel B, Klockener T, Alessi D, Kloppenburg P, Bruning JC. PDK1 deficiency in POMC-expressing cells reveals FoxO1-dependent and -independent pathways in control of energy homeostasis and stress response. Cell Metab. 2008;7:291–301. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.01.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
