How NaCl raises blood pressure: a new paradigm for the pathogenesis of salt-dependent hypertension
- PMID: 22058154
- PMCID: PMC3311458
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00899.2011
How NaCl raises blood pressure: a new paradigm for the pathogenesis of salt-dependent hypertension
Abstract
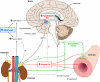
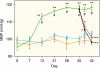
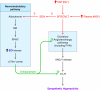
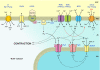
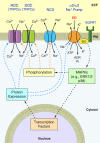
Excess dietary salt is a major cause of hypertension. Nevertheless, the specific mechanisms by which salt increases arterial constriction and peripheral vascular resistance, and thereby raises blood pressure (BP), are poorly understood. Here we summarize recent evidence that defines specific molecular links between Na(+) and the elevated vascular resistance that directly produces high BP. In this new paradigm, high dietary salt raises cerebrospinal fluid [Na(+)]. This leads, via the Na(+)-sensing circumventricular organs of the brain, to increased sympathetic nerve activity (SNA), a major trigger of vasoconstriction. Plasma levels of endogenous ouabain (EO), the Na(+) pump ligand, also become elevated. Remarkably, high cerebrospinal fluid [Na(+)]-evoked, locally secreted (hypothalamic) EO participates in a pathway that mediates the sustained increase in SNA. This hypothalamic signaling chain includes aldosterone, epithelial Na(+) channels, EO, ouabain-sensitive α(2) Na(+) pumps, and angiotensin II (ANG II). The EO increases (e.g.) hypothalamic ANG-II type-1 receptor and NADPH oxidase and decreases neuronal nitric oxide synthase protein expression. The aldosterone-epithelial Na(+) channel-EO-α(2) Na(+) pump-ANG-II pathway modulates the activity of brain cardiovascular control centers that regulate the BP set point and induce sustained changes in SNA. In the periphery, the EO secreted by the adrenal cortex directly enhances vasoconstriction via an EO-α(2) Na(+) pump-Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger-Ca(2+) signaling pathway. Circulating EO also activates an EO-α(2) Na(+) pump-Src kinase signaling cascade. This increases the expression of the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger-transient receptor potential cation channel Ca(2+) signaling pathway in arterial smooth muscle but decreases the expression of endothelial vasodilator mechanisms. Additionally, EO is a growth factor and may directly participate in the arterial structural remodeling and lumen narrowing that is frequently observed in established hypertension. These several central and peripheral mechanisms are coordinated, in part by EO, to effect and maintain the salt-induced elevation of BP.
Figures
References
-
- Abarquez RF., Jr Digitalis in the treatment of hypertension. A prelminary report. Acta Med Philipp 3: 161–170, 1967 - PubMed
-
- Abboud FM. The sympathetic system in hypertension. State-of-the-art review. Hypertension 4: 208–225, 1982 - PubMed
-
- Aileru AA, De Albuquerque A, Hamlyn JM, Manunta P, Shah JR, Hamilton MJ, Weinreich D. Synaptic plasticity in sympathetic ganglia from acquired and inherited forms of ouabain-dependent hypertension. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 281: R635–R644, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Amin MS, Wang HW, Reza E, Whitman SC, Tuana BS, Leenen FH. Distribution of epithelial sodium channels and mineralocorticoid receptors in cardiovascular regulatory centers in rat brain. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 289: R1787–R1797, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

