2,4-Diamino-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-1-ium tetra-fluoro-borate
- PMID: 22058813
- PMCID: PMC3201368
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811038797
2,4-Diamino-6-methyl-1,3,5-triazin-1-ium tetra-fluoro-borate
Abstract
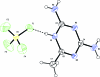
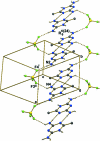
In the crystal structure of the title salt, C(4)H(8)N(5) (+)·BF(4) (-), centrosymmetrically related cations undergo base pairing via a pair of N-H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming an R(2) (2)(8) ring motif. The cations and anions inter-act via N-H⋯F hydrogen bonds, generating supra-molecular layers parallel to ([Formula: see text]20), which are in turn linked into a three-dimensional network, forming rings of R(6) (6)(24) graph-set motif. The crystal structure is further stabilized by π-π stacking inter-actions [centroid-centroid distance = 3.3361 (12) Å].
Figures

References
-
- Balasubramani, K., Muthiah, P. T. & Lynch, D. E. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o2966.
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N. L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Conant, J. W., Corrigan, L. I. & Sparks, R. A. (1964). Acta Cryst. 17, 1085.
-
- Etter, M. C. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res. 23, 120–126.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
