2-(5,6-Dihydro-benzimidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-6-yl)phenol
- PMID: 22058910
- PMCID: PMC3200611
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811030583
2-(5,6-Dihydro-benzimidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-6-yl)phenol
Abstract
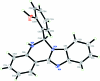
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C(20)H(15)N(3)O, contains two independent mol-ecules, each of which is disordered over two sets of sites corresponding to a rotation of approximately 180° of the dihydro-benzimidazoquinazoline moiety, with refined site occupancies of 0.7479 (13) and 0.2521 (12) for both mol-ecules. The pyrimidine rings are in sofa conformations. In one mol-ecule, the hy-droxy-substituted benzene ring forms dihedral angles of 83.9 (3) and 82.4 (4)° for the major and minor components, respectively, with the mean plane of the benzimidazole ring system. The corres-ponding dihedral angles in the other mol-ecule are 88.31 (14) and 85.8 (6)°. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked via inter-molecular O-H⋯N and N-H.·O hydrogen bonds into chains along [100].
Figures

References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Barreca, M. L., Chimirri, A., De Clercq, E., De Luca, L., Monforte, A.-M., Monforte, P., Rao, A. & Zappalà, M. (2003). Farmaco, 58, 259–263. - PubMed
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
-
- Demirayak, S., Abu Mohsen, U. & Cagri Karaburun, A. (2002). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 37, 255–260. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
