Extracellular/circulating microRNAs and their potential role in cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 22059153
- PMCID: PMC3207246
Extracellular/circulating microRNAs and their potential role in cardiovascular disease
Abstract
microRNAs (miRs, miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that regulate hundreds of gene expression. Numerous studies have demonstrated that miRNAs are not only found intracellularly, but also detectable outside cells, including various body fluids (i.e. serum, plasma, saliva, urine, breast milk, and tears). Interestingly, ~90% of extracellular miRNAs are packaged with proteins (i.e. Ago2, HDL, and other RNA-binding proteins) and ~10% are wrapped in small membranous particles (i.e. exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies). It is believed that these extracellular miRNAs mediate cell-to-cell communication. Recent studies further indicated that the level and composition of these extracellular/circulating miRNAs correlated well with disease or injurious conditions. Uncovering the potential role of extracellular miRNAs in the heart is just emerging. This review will highlight recent exciting findings in the regulation of miRNA biogenesis and secretion, their functional roles in paracrine signaling, and the potential as non-invasive biomarkers for cardiovascular disease.
Figures

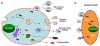
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. microRNAs: Tiny regulators with great potential. Cell. 2001;107:823–826. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:102–114. - PubMed
-
- Eulalio A, Huntzinger E, Izaurralde E. Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell. 2008;132:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Fazi F, Nervi C. MicroRNA: Basic mechanisms and transcriptional regulatory networks for cell fate determination. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79:553–561. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
