Decitabine immunosensitizes human gliomas to NY-ESO-1 specific T lymphocyte targeting through the Fas/Fas ligand pathway
- PMID: 22060015
- PMCID: PMC3229551
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-192
Decitabine immunosensitizes human gliomas to NY-ESO-1 specific T lymphocyte targeting through the Fas/Fas ligand pathway
Abstract
Background: The lack of effective treatments for gliomas makes them a significant health problem and highlights the need for the development of novel and innovative treatment approaches. Immunotherapy is an appealing strategy because of the potential ability for immune cells to traffic to and destroy infiltrating tumor cells. However, the absence of well-characterized, highly immunogenic tumor-rejection antigens (TRA) in gliomas has limited the implementation of targeted immune-based therapies.
Methods: We hypothesized that treatment with the demethylating agent, decitabine, would upregulate the expression of TRA on tumor cells, thereby facilitating enhanced surveillance by TRA-specific T cells.
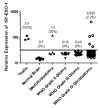
Results and discussion: Treatment of human glioma cells with decitabine increased the expression of NY-ESO-1 and other well characterized cancer testes antigens. The upregulation of NY-ESO-1 made these tumors susceptible to NY-ESO-1-specific T-cell recognition and lysis. Interestingly, decitabine treatment of T98 glioma cells also sensitized them to Fas-dependent apoptosis with an agonistic antibody, while a Fas blocking antibody could largely prevent the enhanced functional recognition by NY-ESO-1 specific T cells. Thus, decitabine treatment transformed a non-immunogenic glioma cell into an immunogenic target that was efficiently recognized by NY-ESO-1--specific T cells.
Conclusions: Such data supports the hypothesis that agents which alter epigenetic cellular processes may "immunosensitize" tumor cells to tumor-specific T cell-mediated lysis.
Figures



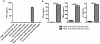

References
-
- Deorah S, Lynch CF, Sibenaller ZA, Ryken TC. Trends in brain cancer incidence and survival in the United States: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program, 1973 to 2001. Neurosurg Focus. 2006;20:E1. - PubMed
-
- Liau LM, Prins RM, Kiertscher SM, Odesa SK, Kremen TJ, Giovannone AJ, Lin JW, Chute DJ, Mischel PS, Cloughesy TF, Roth MD. Dendritic cell vaccination in glioblastoma patients induces systemic and intracranial T-cell responses modulated by the local central nervous system tumor microenvironment. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:5515–5525. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0464. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

