Interferometric methods for label-free molecular interaction studies
- PMID: 22060037
- PMCID: PMC4317347
- DOI: 10.1021/ac202812h
Interferometric methods for label-free molecular interaction studies
Figures
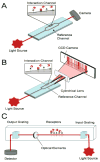


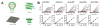
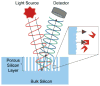


References
-
- Herschel W. Philos Trans R Soc, London. 1805;95:31–64.
-
- Baldwin JE, Haniff CA. Philos Trans: Math, Phys Eng Sci. 2002;360:969–986. - PubMed
-
- Michelson AA, Pease FG. Astrophys J. 1921;53:249–259.
-
- Bruning JH, Herriott DR, Gallaghe Je, Rosenfel Dp, White AD, Brangacc DJ. Appl Opt. 1974;13:2693–2703. - PubMed
-
- Scudieri F. Appl Opt. 1980;19:404–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

