Wip1 promotes RUNX2-dependent apoptosis in p53-negative tumors and protects normal tissues during treatment with anticancer agents
- PMID: 22065775
- PMCID: PMC3258624
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1107017108
Wip1 promotes RUNX2-dependent apoptosis in p53-negative tumors and protects normal tissues during treatment with anticancer agents
Abstract
The inactivation of the p53 tumor suppressor pathway in many cancers often increases their resistance to anticancer therapy. Here we show that a previously proposed strategy directed to Wip1 inhibition could be ineffective in tumors lacking p53. On the contrary, Wip1 overexpression sensitized these tumors to chemotherapeutic agents. This effect was mediated through interaction between Wip1 and RUNX2 that resulted, in response to anticancer treatment, in RUNX2-dependent transcriptional induction of the proapoptotic Bax protein. The potentiating effects of Wip1 overexpression on chemotherapeutic agents were directed only to tumor cells lacking p53. The overexpression of Wip1 in normal tissues provided protection from cisplatin-induced apoptosis through decreased strength of upstream signaling to p53. Thus, Wip1 phosphatase promotes apoptosis in p53-negative tumors and protects normal tissues during treatment with anticancer agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
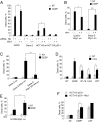

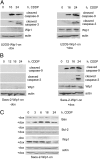
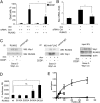
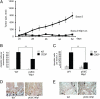
References
-
- Harris SL, Levine AJ. The p53 pathway: Positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 2005;24:2899–2908. - PubMed
-
- Martin AC, et al. Integrating mutation data and structural analysis of the TP53 tumor-suppressor protein. Hum Mutat. 2002;19:149–164. - PubMed
-
- Bond GL, Hu W, Levine AJ. MDM2 is a central node in the p53 pathway: 12 years and counting. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005;5:3–8. - PubMed
-
- Lu X, et al. The Wip1 Phosphatase acts as a gatekeeper in the p53-Mdm2 autoregulatory loop. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:342–354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

