Beyond cAMP: The Regulation of Akt and GSK3 by Dopamine Receptors
- PMID: 22065948
- PMCID: PMC3206544
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00038
Beyond cAMP: The Regulation of Akt and GSK3 by Dopamine Receptors
Abstract
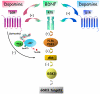
Brain dopamine receptors have been preferred targets for numerous pharmacological compounds developed for the treatment of various neuropsychiatric disorders. Recent discovery that D2 dopamine receptors, in addition to cAMP pathways, can engage also in Akt/GSK3 signaling cascade provided a new framework to understand intracellular signaling mechanisms involved in dopamine-related behaviors and pathologies. Here we review a recent progress in understanding the role of Akt, GSK3, and related signaling molecules in dopamine receptor signaling and functions. Particularly, we focus on the molecular mechanisms involved, interacting partners, role of these signaling events in the action of antipsychotics, psychostimulants, and antidepressants as well as involvement in pathophysiology of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and Parkinson's disease. Further understanding of the role of Akt/GSK3 signaling in dopamine receptor functions could provide novel targets for pharmacological interventions in dopamine-related disorders.
Keywords: Akt; G protein coupled receptor; arrestin; catecholamines; dopamine; glycogen synthase kinase 3; protein kinase B; receptor tyrosine kinase.
Figures


References
-
- Aleyasin H., Rousseaux M. W., Marcogliese P. C., Hewitt S. J., Irrcher I., Joselin A. P., Parsanejad M., Kim R. H., Rizzu P., Callaghan S. M., Slack R. S., Mak T. W., Park D. S. (2010). DJ-1 protects the nigrostriatal axis from the neurotoxin MPTP by modulation of the AKT pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 3186–319110.1073/pnas.0914876107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

