Gout, genetics and ABC transporters
- PMID: 22065982
- PMCID: PMC3206739
- DOI: 10.3410/B3-23
Gout, genetics and ABC transporters
Abstract
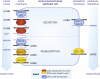
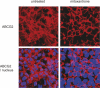
Gout is a chronic arthritic disease associated with high levels of urate in blood. Recent advances in research have permitted the identification of several new and common genetic factors underlying the disease. Among them, a polymorphism in the ABC transporter gene ATP-binding cassette transporter isoform G2 has been highlighted. ATP-binding cassette transporter isoform G2 was found to be involved in renal urate elimination, and the presence of the Q141K polymorphism to induce a 2-fold decrease in urate efflux. The Q141K variant has been shown to have impaired trafficking, leading to its intracellular retention, whereas the wild type protein is expressed on the cell surface. Several agents are being studied for the purpose of improving folding, trafficking and function of various ABC transporters, including ATP-binding cassette transporter isoform G2. If successful, this strategy opens doors to potential new therapies for gout.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of ABCG2 in the Pathogenesis of Primary Hyperuricemia and Gout-An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 22;22(13):6678. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136678. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34206432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Recent progress and prospects for research on urate efflux transporter ABCG2].Nihon Rinsho. 2014 Apr;72(4):757-65. Nihon Rinsho. 2014. PMID: 24796111 Review. Japanese.
-
ABCG2 as a therapeutic target candidate for gout.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Feb;22(2):123-129. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1420167. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 29264928 Review.
-
Effects of the gout-causing Q141K polymorphism and a CFTR ΔF508 mimicking mutation on the processing and stability of the ABCG2 protein.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Jul 19;437(1):140-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.06.054. Epub 2013 Jun 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23800412
-
ABCG2 dysfunction increases the risk of renal overload hyperuricemia.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2014;33(4-6):266-74. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2013.866679. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2014. PMID: 24940678
Cited by
-
Genetic variation in the ABCG2 gene is associated with gout risk in the Chinese Han population.Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Jan;35(1):159-63. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-3105-9. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26506822
-
Dieting alleviates hyperuricemia and organ injuries in uricase-deficient rats via down-regulating cell cycle pathway.PeerJ. 2023 Sep 8;11:e15999. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15999. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37701826 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal tract is an important organ for lowering serum uric acid in rats.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 21;12(12):e0190194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190194. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29267361 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of chronic kidney disease on long-term outcome of patients with valvular heart defects.Int Urol Nephrol. 2020 Nov;52(11):2161-2170. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02561-4. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Int Urol Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32661631 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic evidence for a dramatic functional transition of the malpighian tubules after a blood meal in the Asian tiger mosquito Aedes albopictus.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Jun 5;8(6):e2929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002929. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24901705 Free PMC article.

